Technical Overview: Oracle Cloud VMware Solution
Introduction
Oracle Cloud VMware Solution (OCVS) allows customers to build VMware SDDC stack on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). With this, customers can easily migrate VMware workloads to the public cloud without refactoring application workloads or toolsets. This enables VMware workloads to access public cloud services and benefits from the scale and agility offered by public cloud infrastructure.
- Deploy VMware SDDC stack in OCI.
- Migrate VMware workloads to OCI.
- Seamless access to OCI Services.

SDDC Bundle Specification
OCVS VMware SDDC bundle includes the following VMware products and solutions. These products are included in OCVS pricing SKUs.
| Product Name | Product Version | License |
| VMware vSphere | VMware vSphere 7 Update 3 | vSphere 7 Enterprise |
| VMware vSAN | VMware vSAN 7 Update 3 | vSAN 7 Enterprise |
| VMware NSX-T Data Center | VMware NSX-T Data Center 3.2 | NSX Data Center Enterprise Plus |
| VMware HCX | VMware HCX 4.5 | VMware HCX Advance |
VMware Attached Services on OCVS
Oracle Cloud VMware Solution includes all the VMware products mentioned above. However, you can always extend OCVS VMware SDDC to other VMware products and services. These VMware products and services can be directly purchased from VMware. The following VMware products and solutions are certified on Oracle Cloud VMware Solution.
- VMware Site Recovery Manager
- VMware Horizon
- VMware Aria
- VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid
- VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer (NSX ALB)
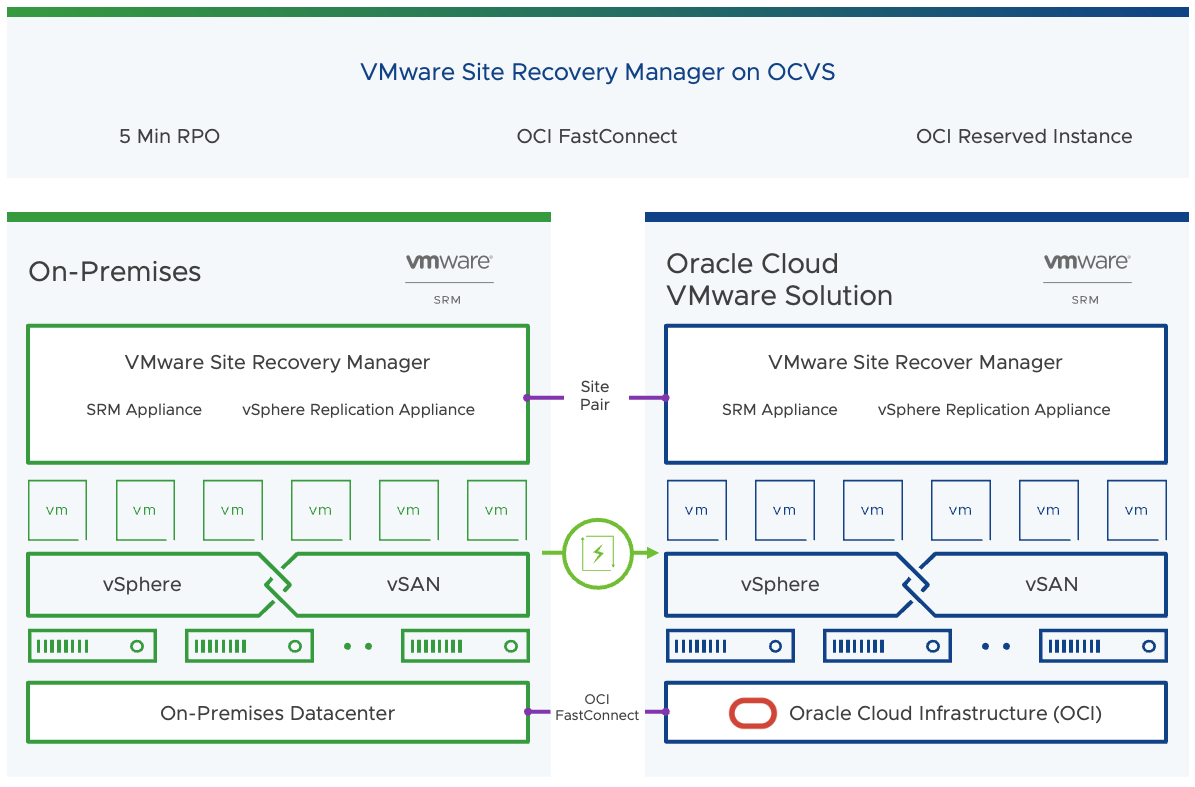
VMware Site Recovery Manager on OCVS
VMware Site Recovery Manager for Oracle Cloud VMware Solution is an attached service that customers can purchase to deploy VMware SRM on OCVS VMware SDDC. This allows customers to build a DR infrastructure on OCVS and help them orchestrate the failover and failback of virtual machine between the on-premises and OCVS environment.
The advantages of having an OCVS environment as the DR site are the following-
- Scale and agility or Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Access to OCI reserved instances
- Low-cost storage options with OCI File System and OCI Block Storage Volume service
- Support for multi-site DR environment, protecting workloads from multiple VMware sites on a single DR environment on OCVS.
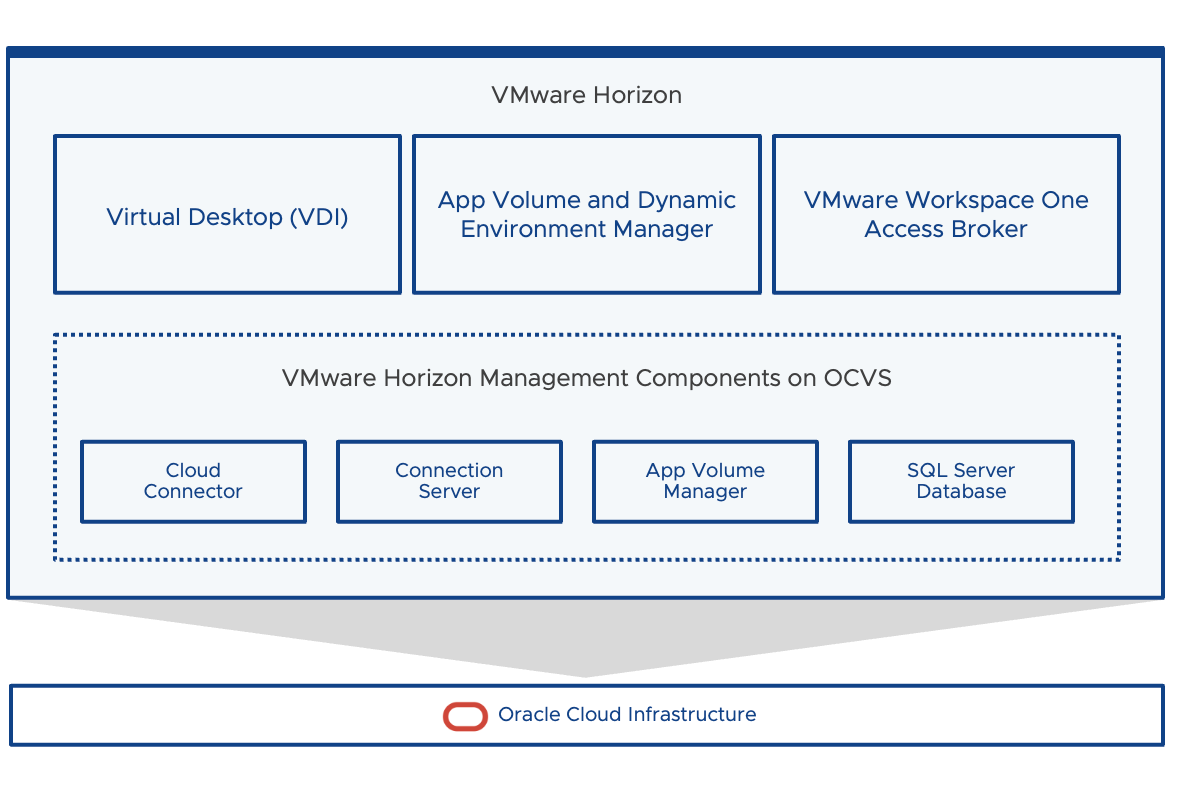
VMware Horizon on OCVS
VMware Horizon on Oracle Cloud VMware Solution delivers a seamlessly integrated hybrid cloud for virtual desktops and applications. Horizon on Oracle Cloud VMware Solution lets you leverage the same VMware tools and skillsets to manage virtual desktop environments. This also gives access to cloud infrastructure resources that you can use to scale horizon and SDDC resources on-demand. Horizon on OCVS has a consolidated architecture which means that all the Horizon appliances and management components are deployed on the same VMware SDDC stack.
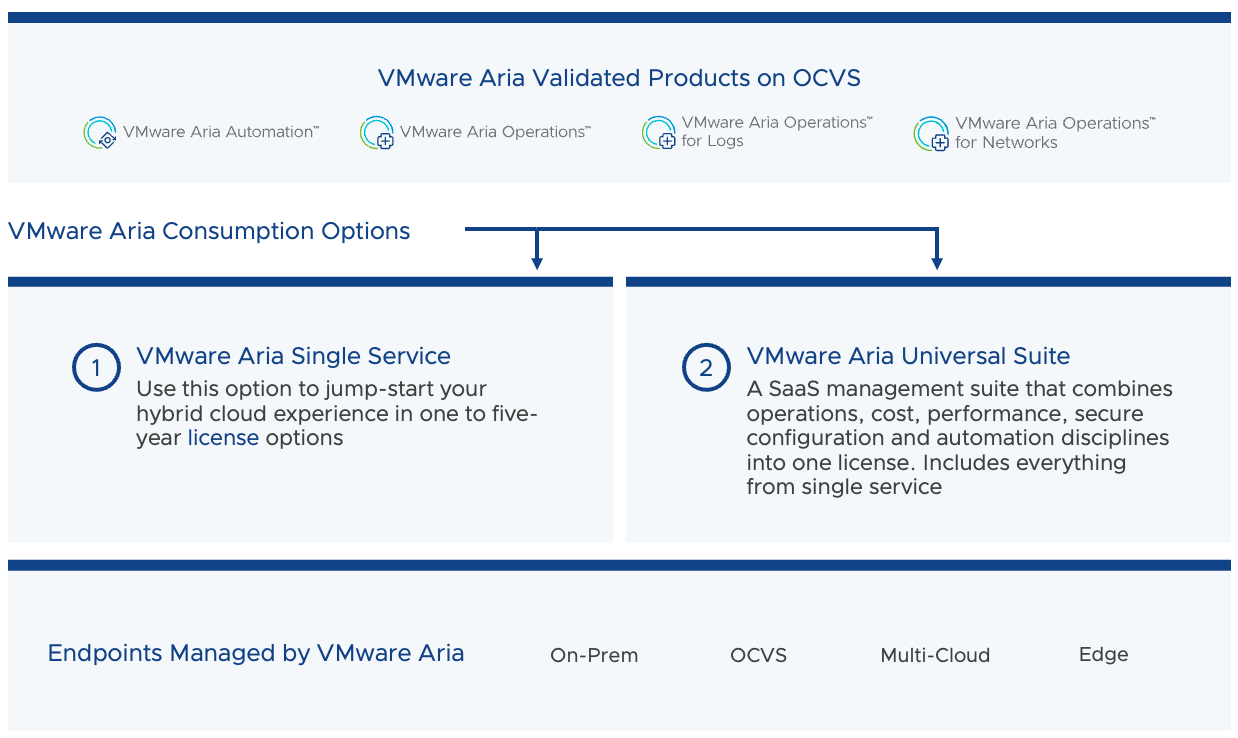
VMware Aria on OCVS
VMware Aria is a multi-cloud management portfolio that consistently deploys and operates your apps, infrastructure, and platform services across private, hybrid, and multiple clouds with a common data model. Customers can now consume and configure OCVS VMware SDDC as the management endpoint in VMware Aria.
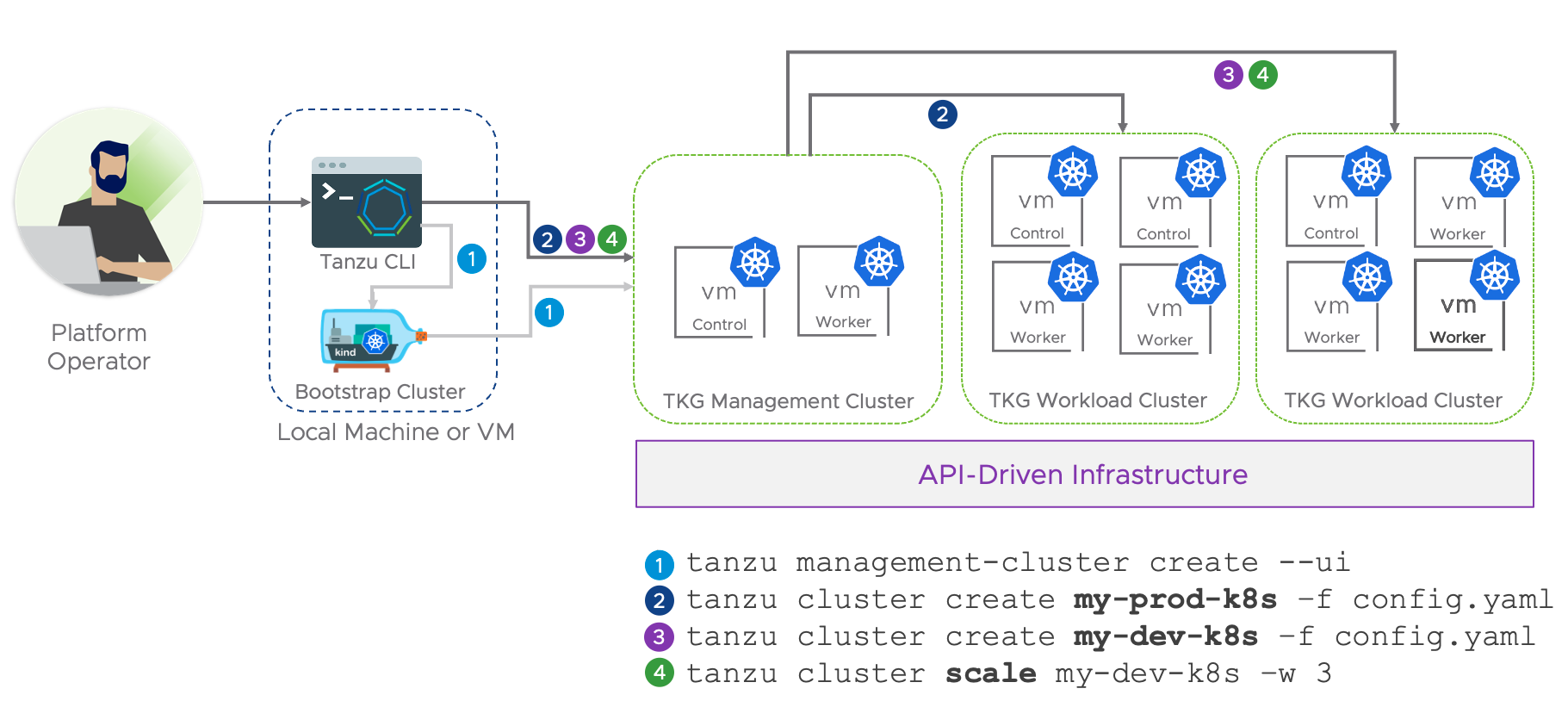
VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid OCVS
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid allows you to deploy cloud-native apps on VMware-based environments such as on-premises, private cloud, or OCVS. With the recent validation of Tanzu Kubernetes Grid on OCVS, you can now deploy the TKG cluster on the OCVS VMware SDDC instance and take advantage of VMware Tanzu to modernize your application workloads.
VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer (NSX ALB)
VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer (Avi) is an API (Application Programming Interface) first, self-service Multi-Cloud Application Services Platform that ensures consistent application delivery, bringing software load balancers, web application firewall (WAF), and container Ingress for applications across data centers and clouds. NSX ALB is now supported and can be deployed on OCVS VMware SDDC to meet the advanced load balancing requirements.
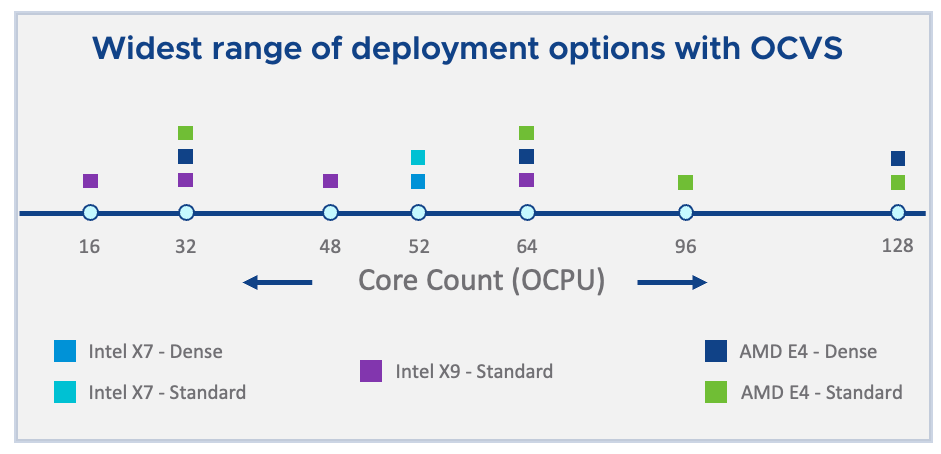
OCVS Compute Shapes
Oracle Cloud VMware Solution offers the widest range of compute shapes to meet all your workload requirements catering to general-purpose workloads, high-performance compute workloads or storage-hungry workloads. These compute shapes are OCI bare metal nodes with different shapes and specifications. There are two types of OCI compute shapes supported on OCVS.
- OCI Dense I/O Compute Shape
- OCI Standard Compute Shape
OCI Dense I/O Compute Shape
OCI DenseIO shapes are designed for large databases, big data workloads, and applications that require high-performance locally attached storage. In OCVS, DenseIO compute shapes come with locally attached NVMe drives to create the vSAN cluster.
| OCI Shape | Processor | Core | Memory | Storage | Network |
| BM.DenseIO2.52 | Intel Xeon Platinum 8167M X7 (Skylake) | 52 | 768 GB | 51.2 TB | 50 Gbps |
| BM.DenseIO2.E4.128 | AMD EPYC 7J13 (3rd Gen) | 32/64/128 | 2048 GB | 54.2 TB | 100 Gbps |
Note: vSAN is the primary storage for OCVS VMware SDDC backed by OCI Dense I/O compute shapes.
OCI Standard Compute Shape
OCI Standard Standard shapes are designed for general-purpose workloads and suitable for a wide range of applications and use cases. They provide a balance of cores, memory, and network resources. Standard compute shapes doesn’t come with any locally attached storage, rather they rely on external storage such as OCI FS and OCI block volume to meet the VMware SDDC storage requirements.
| OCI Shape | Processor | Core | Memory | Storage | Network |
| BM.Standard2.52 | Intel Xeon Platinum 8167M X7 (Skylake) | 52 | 768 GB | Only External Storage | 50 Gbps |
| BM.Standard3.64 | Intel Xeon Platinum 8358 X9 (Icelake) | 16/32/48/64 | 1024 GB | Only External Storage | 100 Gbps |
| BM.Standard.E4.128 | AMD EPYC 7J13 (3rd Gen) | 32/64/96/128 | 2048 GB | Only External Storage | 100 Gbps |
OCVS Storage Overview
OCVS supports all the major VMware storage formats which are vSAN, VMFS, and NFS. Having the support of all vSAN, VMFS, and NFS storage for VMware SDDC gives the required flexibility to choose the right storage depending on the use case.
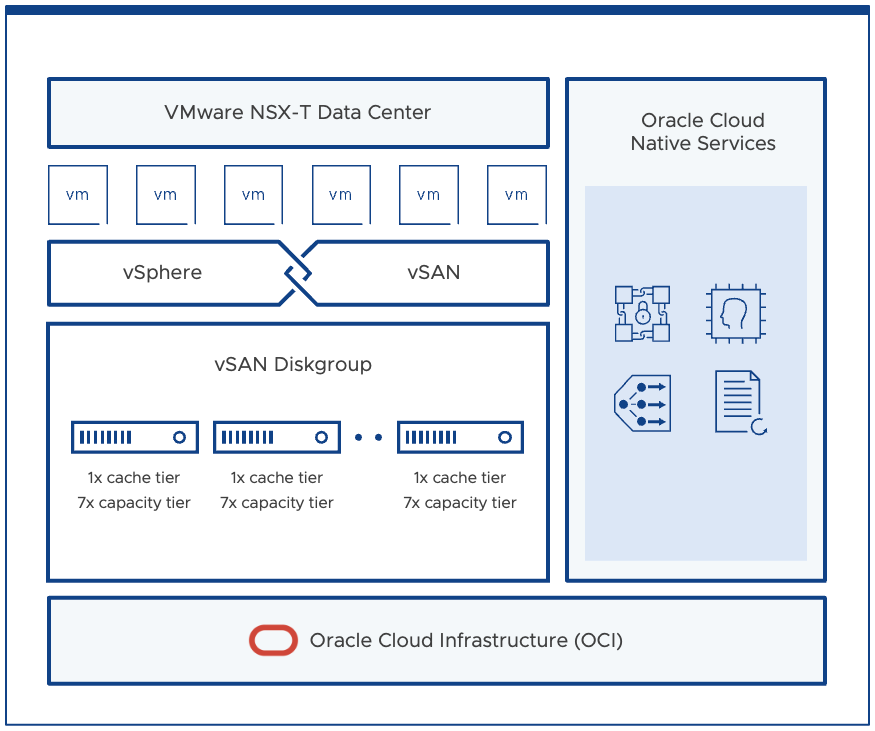
VMware vSAN
VMware vSAN is the primary storage for VMware SDDC backed by OCI Dense IO compute shapes. vSAN on OCVS is a tiered architecture where each node consists of 1x NVMe drive for cache tier and 7x NVMe drives for capacity tier. All these storage devices across the ESXi hosts are pooled together to create a vSAN cluster. The usable capacity depends upon OCI compute shape that is used to create VMware SDDC in OCVS. With BM.DenseIO2.52 you can get ~122 TB and with BM.DenseIO2.E4.128 you can get ~128 TB of usable capacity with minimum 3 node OCVS VMware SDDC deployment.
The vSAN cluster gets bootstrap during the OCVS VMware SDDC build phase and there are no manual steps required configure a vSAN cluster in OCVS.
Key Highlights
- Primary storage for DenseIO compute shapes
- Highest storage resource footprint compared to other VMware hyperscaler solutions.
- Leverage all the vSAN Enterprise features on the go.
- Full flash storage architecture for better performance.
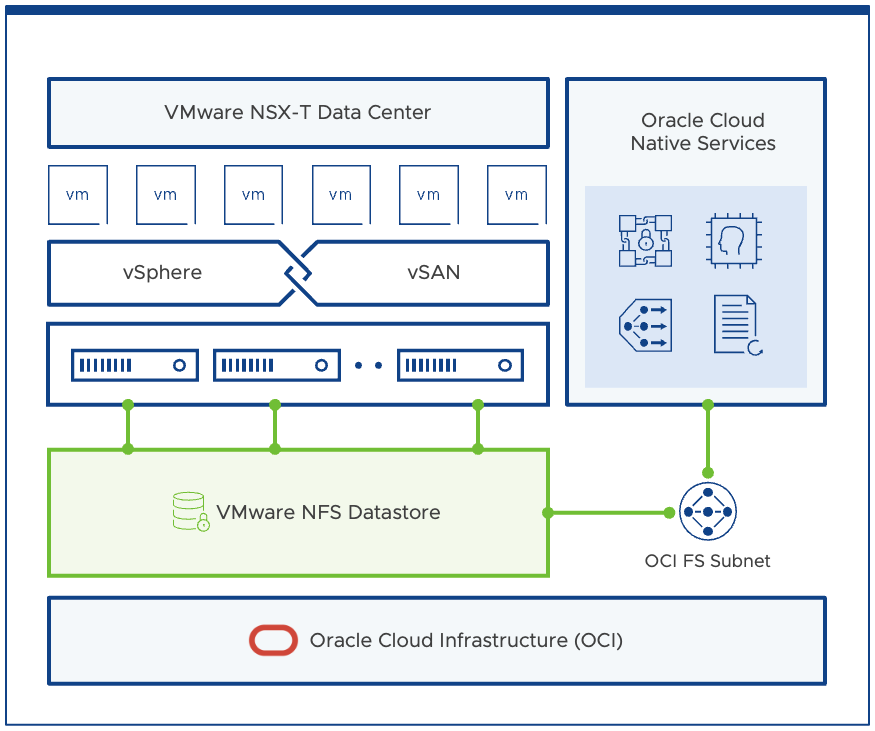
OCI File Storage Service
OCI File Storage Service provides a secure, scalable, enterprise-grade network file system. With this, you can export NFSv3 file export to any NFS client, including VMware ESXi.
Oracle has announced the support of Oracle Cloud File Storage Service (FSS) for OCVS. Making it primary storage for OCVS VMware SDDC backed by standard compute shapes and secondary storage for OCVS VMware SDDC backed by Dense IO compute shapes.
Key Highlights
- Secondary storage for DenseIO compute shapes.
- NFSv3 protocol.
- Scale storage resources independently with compute nodes.
- Low-cost storage option.
OCI Block Storage Volume
OCI Block storage volume service allows customers to export iSCSI block volumes. This service is also certified on OCVS VMware SDDC, thus allowing customers to deploy VMware VMFS datastores using OCI Block Storage Volume Service.
This is the primary storage for OCVS VMware SDDCs backed by OCI Standard compute shapes and a secondary storage option for OCI DenseIO compute shapes. The OCI Block Storage Volume supports a
maximum of 300,000 IOPS per volume with ultra-high-performance storage tier.
Key Highlights
- Primary storage for standard compute shapes.
- Secondary storage for DenseIO compute shapes.
- iSCSI protocol.
- Support for ultra-high-performance tier with 300,000 IOPS per volume.
- Scale storage resources independently with compute nodes.

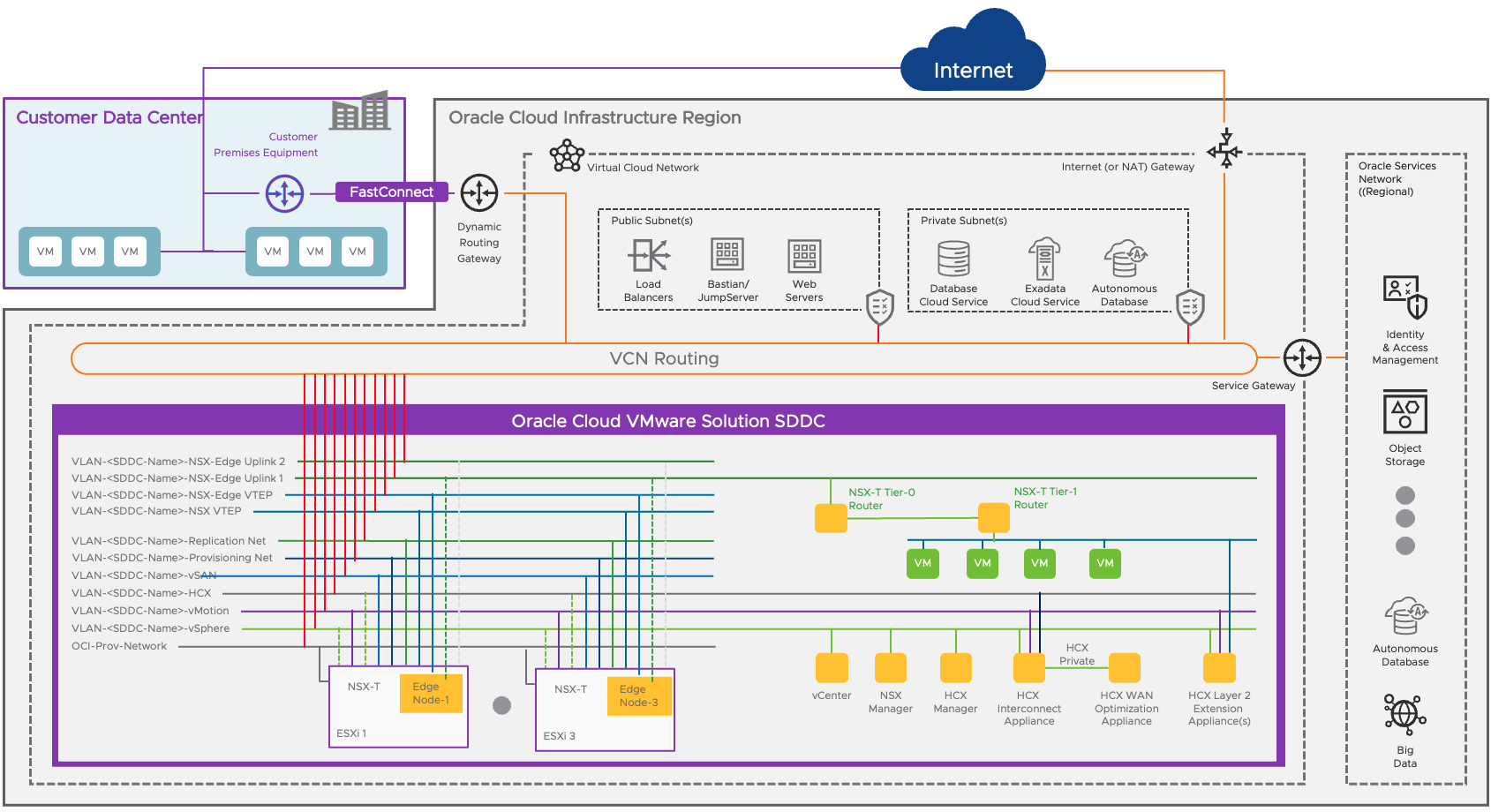
OCVS Networking Design
Oracle Cloud VMware Solution is a native OCI solution and leverage core OCI networking constructs such as Virtual Cloud Network, Gateways, Security rules, and route table to establish the networking resources for OCVS solution. Let’s look at some of these networking resources in details.
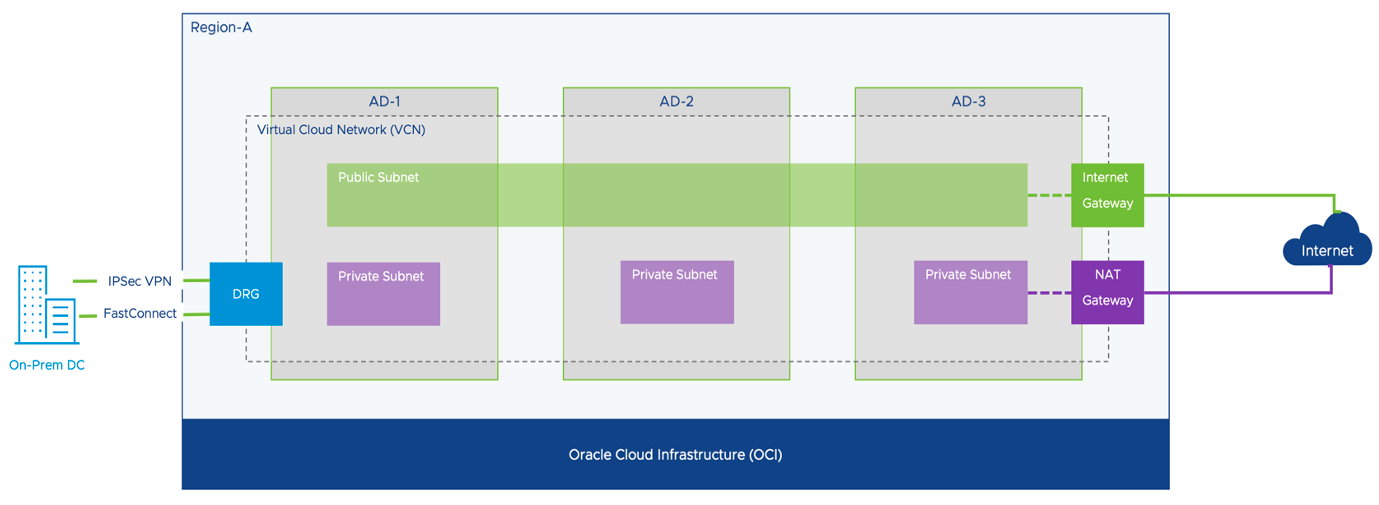
- VCN, aka Virtual Cloud Network, is a virtual, private network that you set up in OCI.
- Public Subnet can have both Inbound/Outbound communication to the Internet through Internet Gateway
- Private Subnet can have only Outbound communication to the internet through NAT Gateway
- Subnets can be region-wide or AD-wide Subnet
- Dynamic Routing Gateway allows you to connect to the On-Prem DC
OCVS deployment workflow creates a private subnet for VMware SDDC. The recommended size for private subnet is /21 and this allows the workflow to create other VMware SDDC networks to support a variety of traffic. Below are the networks that gets created as a part of build workflow.
| Network Name | Purpose |
| Provisioning/ Management | The ESXi management interface (vmk0) resides on this subnet. |
| Replication | Used for the vSphere Replication engine. (VMware version 7. x only)
|
| vSphere | This VLAN is used for management components of Oracle Cloud VMware Solution such as vCenter Server, NSX Manager, and NSX Edge. |
| vMotion | This VLAN is used for VMware vMotion migration of the management and customer workload components. |
| vSAN | This VLAN is used for vSAN (VMware storage) data traffic. |
| NSX VTEP | This VLAN is used for data plane traffic between ESXi hosts. |
| NSX Edge | VTEP This VLAN is used for data plane traffic between the ESXi host and NSX Edge. |
| NSX Edge Uplink 1 | This VLAN is used for communication between the VMware SDDC and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. |
| NSX Edge Uplink 2 | This VLAN is reserved for future deployment of public-facing applications on the VMware SDDC. |
| HCX | (Optional) This VLAN is used for HCX traffic. Create it if you plan to enable HCX when you provision the SDDC. |
Authors and Contributors
A list of authors and contributors should be listed here in the following format:
- Jatin Purohit, Sr. Technical Marketing Architect, VMware
