Testing Recovery Plan for VMware Site Recovery for Google Cloud VMware Engine
Testing a Recovery Plan
When you create or modify a recovery plan, best practice is to test it before attempting a planned migration or for disaster recovery.
By testing a recovery plan, you ensure that the virtual machines that the plan protects recover correctly to the recovery site. If you do not test recovery plans, an actual disaster recovery situation might not recover all virtual machines, potentially resulting in data loss.
Testing a recovery plan exercises nearly every aspect of a recovery plan, although Site Recovery Manager makes several concessions to avoid disrupting ongoing operations on the protected and recovery sites. Recovery plans that suspend local virtual machines do so for tests and for actual recoveries. With this exception, running a test recovery does not disrupt replication or ongoing activities at either site.
If you use vSphere Replication, when you test a recovery plan, the virtual machine on the protected site can still synchronize with the replica virtual machine disk files on the recovery site. The vSphere Replication Server creates redo logs on the virtual machine disk files on the recovery site, so that synchronization can continue normally. When you perform a clean-up after running a test, the vSphere Replication Server removes the redo logs from the disks on the recovery site and persists the changes accumulated in the logs to the VM disks.
You can run test recoveries as often as necessary and can cancel a recovery plan test at any time.
Reprotect
After Site Recovery Manager performs a recovery, the virtual machine's start-up on the recovery site. By running reprotect when the protected site comes back online, you reverse the direction of replication to protect the recovered virtual machines on the recovery site back to the original protected site.
Reprotect uses the protection information that you established before a recovery to reverse the direction of protection. You can initiate the reprotect process only after recovery finishes without any errors. If the recovery finishes with errors, you must fix all errors and rerun the recovery, repeating this process until no errors occur.
You can conduct tests after a reprotect operation completes, to confirm that the new configuration of the protected and recovery sites is valid.
- Before performing the reprotect process, note the following:
- You performed a recovery either as part of a planned migration or as part of disaster recovery.
- The original protected site is running.
- You have not run reprotect since the recovery.
- If you performed a disaster recovery, you must perform a planned migration when the hosts and datastores on the original protected site are running again.
Proceed with reprotect only if you meet the above criteria. The reprotect reverses the replication path from the DR site to the production site and then runs the recovery of VMs from the DR site to the production site. In case of any failure during this recovery, you will have an option to do force cleanup.
Note - Force cleanup is only available after you run reprotect once and errors occur. Enabling this option forces the removal of virtual machines, ignore errors, and returns the recovery plan to the ready state.
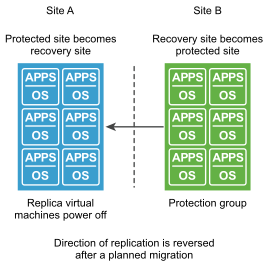
Reprotect results in the reconfiguration of Site Recovery Manager protection groups and recovery plans to work in the opposite direction. After a reprotect operation, you can recover virtual machines back to the original site using a planned migration workflow.
When the planned migration completes, the virtual machines are running on the original protected site but the virtual machines are not protected. The virtual machines on the original recovery site (DR site), are powered off. You must perform a second reprotect operation to start the replication now from the production site to the DR site.
Reports
Site Recovery Manager history reports are useful to diagnose the Site Recovery Manager Server behavior before and after a failure. You can change the number of historical reports to export.
You can view and export reports about each run of a recovery plan, test recovery plan, test cleanup, or perform reprotect.
Recovery plan histories provide information about each run, test, clean up, or reprotect of a recovery plan. The history contains information about the result and the start and end times for the whole plan and for each step in the plan. You can export history at any time, but history always contains entries only for completed operations. If an operation is in progress, the history appears after the operation completes.
Site Recovery Manager preserves history for deleted recovery plans. You can export history reports for existing and deleted plans.
