Replication and Disaster Recovery on VMC on AWS Using Site Recovery Manager
Introduction
Enabling VMware Site recovery
VMware Site recovery is managed service offering on VMware Cloud on AWS. To start consuming VMware Site Recovery Service we need to activate the same from the VMware cloud on AWS console. The prerequisites for enabling Site Recovery service are to verify you have a Software-Defined Data center on VMware Cloud on AWS.
Site Pairing
Choosing a target vCenter for a failover SDDC is simple; each SDDC contains a single vCenter instance. All source vCenters which contain VMs and are protected by the selected group(s) can be mapped to a target vCenter on VMware Cloud on AWS as the selected recovery site.
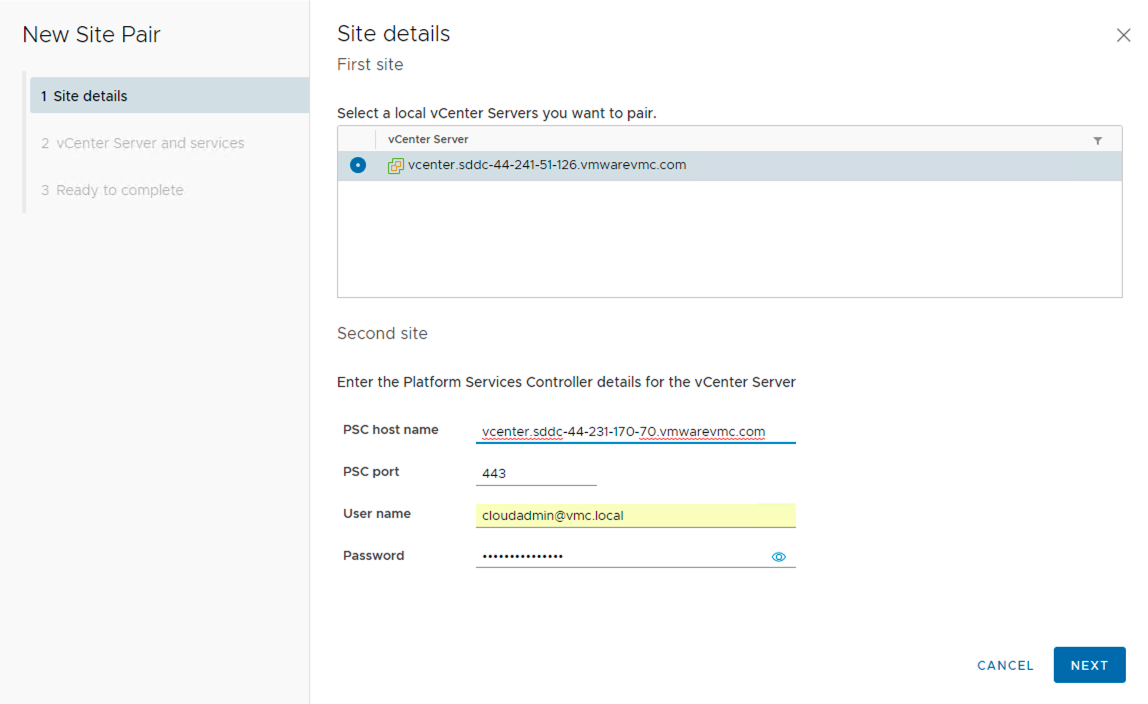
Pairing sites is a simple process.
- Enter the Platform Services Controller details for the vCenter Server with port number and credentials for the secondary site.
- Choose the vCenter and its services.
- Review and complete.
Planning
After the site pairing is configured, you must perform the additional mapping between sites. The mapping wizard has two options to create mappings for Network, Folder and Storage Policy Mapping.
- Automatically prepare mappings with matching names - Here the system automatically prepares mappings for networks with matching names under the selected network containers.
- Prepare mappings manually - Choose this option to manually select which networks to map
Note: Access to manage the Site Recovery Manager site pair and replications are possible only via the private IP of SDDC or when connected via a VPN or direct connect.
The following figure is the Summary page that shows all the required information regarding the paired sites. Ignore the certificate expiry message in the below image.
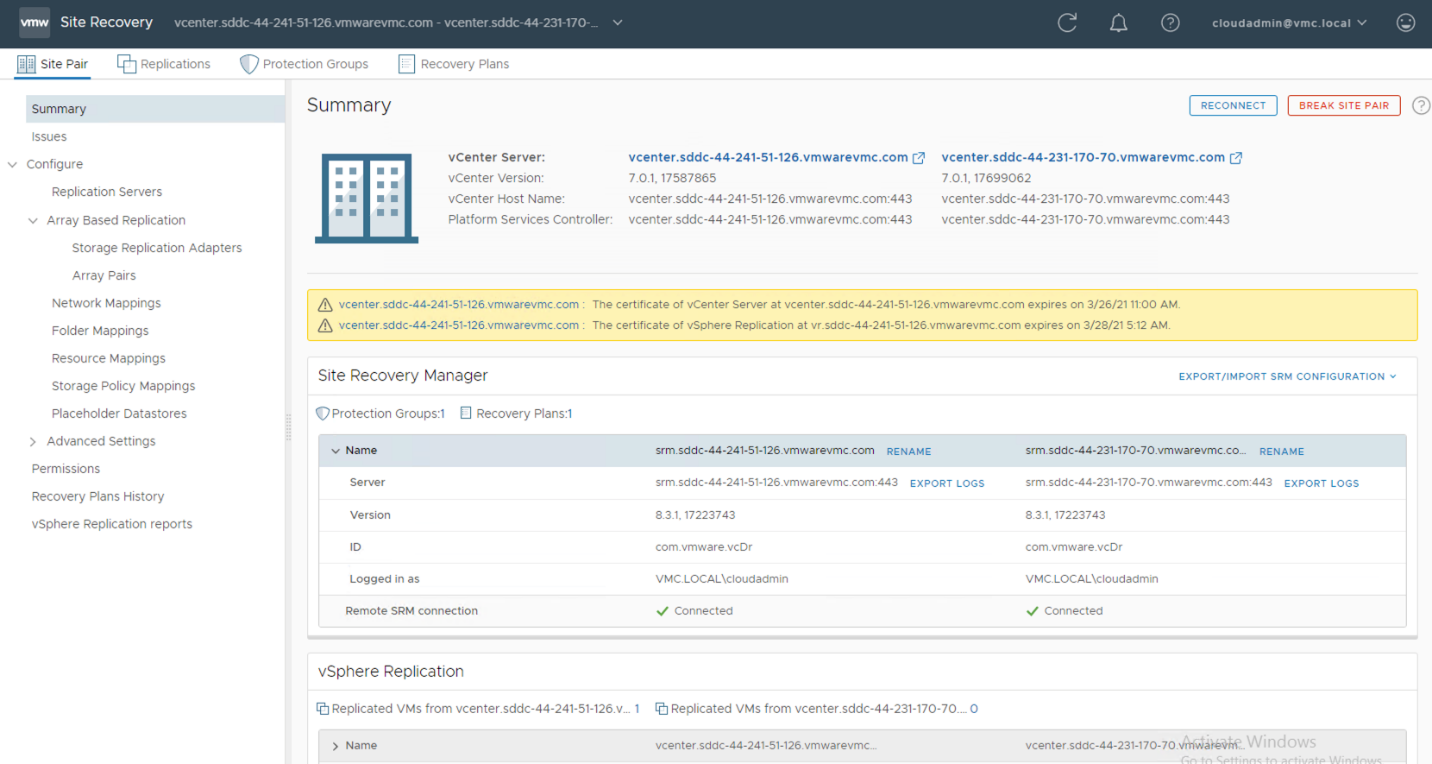
In order to create a DR plan, you must configure several parameters to be run during a recovery. These parameters include the creation of a protection group, replicated VM datastore, inventory mapping (network, resource pool, folder), and more.
Network Mapping
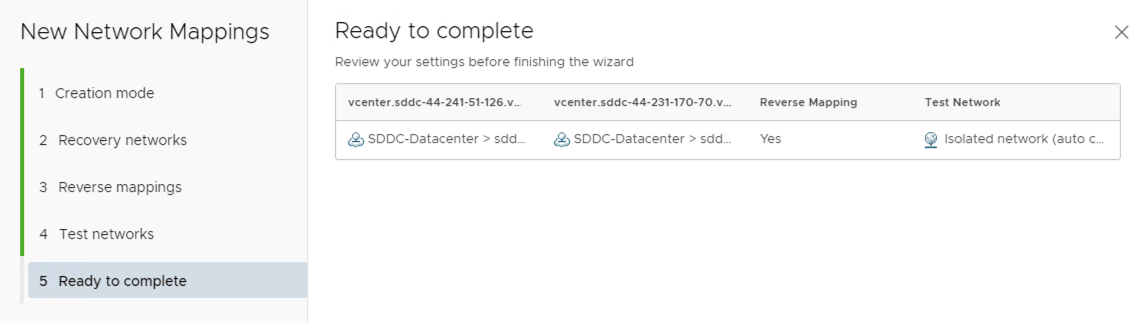
Network mapping consists of three configuration options.
- Recovery Network - used to map the site 1 network labels to site 2 network labels.
- Reverse mapping - flag available to choose if the mapping is also needed to configured bi-directionally as per config in recovery network.
- Test Networks - This option helps determine how the test network needs to be created. This test network is used when test recovery is executed. You can choose to auto-create an isolated network or choose from an existing pre-defined test network.
 If you choose option 1, the network used for Management nodes is excluded and only workload network mapping is performed. This is done to ensure we do not map the SDDC management network.
If you choose option 1, the network used for Management nodes is excluded and only workload network mapping is performed. This is done to ensure we do not map the SDDC management network.
IP Customization
You can customize IP settings for virtual machines for the protected site and the recovery site. Customizing the IP properties of a virtual machine overrides the default IP settings when the recovered virtual machine starts at the destination site.
If you do not customize the IP properties of a virtual machine, Site Recovery Manager uses the IP settings for the recovery site during recovery or test from the protection site to the recovery site. Site Recovery Manager uses the IP settings for the protection site after reprotect during the recovery or a test from the original recovery site to the original protection site.
IP customization is applied on a network mapping level here, this can also be applied at the virtual machine level which is detailed in the later section in this document. Select the network mapping created and click more options(... in the UI) to add the IP range, Gateway, and DNS information to be used during customization for this mapping on applicable virtual machines.
Folder Mapping
The Folder mapping page on the Site pair wizard displays a subset of the vCenter object inventory for both the source and target vCenters. The mapping here corresponds to VM and template view on the SDDC. The flags available in this wizard are:
- Configure recovery folder mappings for one or more folders.
- Select configured mappings for which to automatically create reverse mappings. This might overwrite existing mappings (manually configured in any other mapping created).
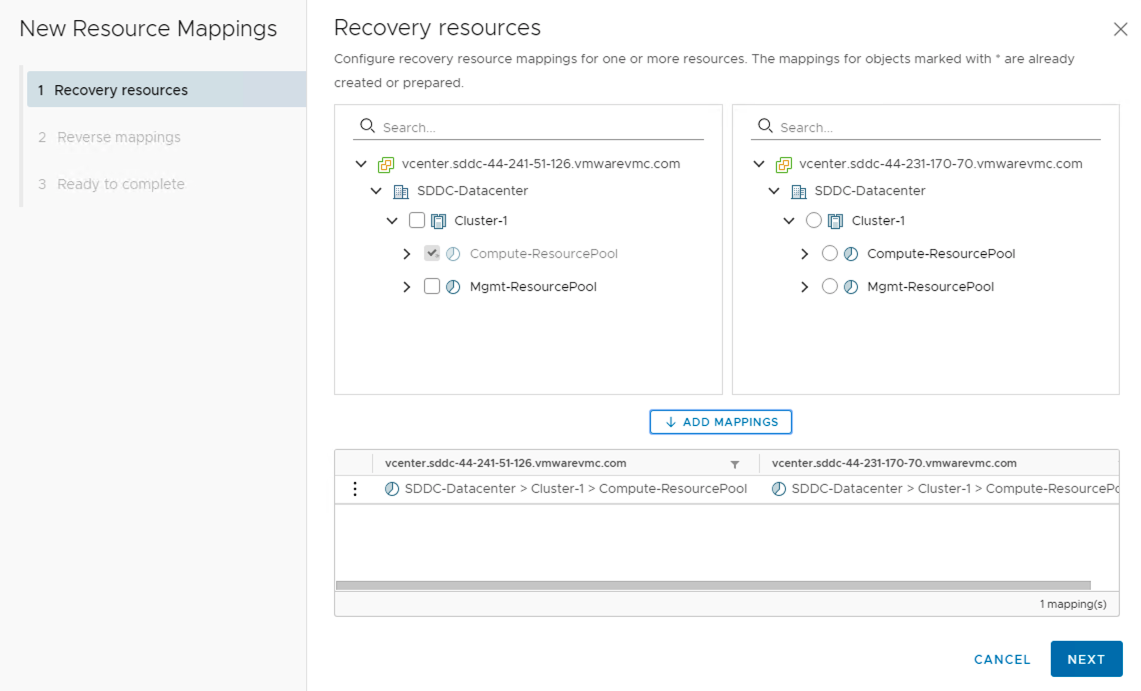
Resource Mapping
Mapping of clusters and resource pools can be configured using the resource mapping options. This wizard ensures the mapping is done by manually choosing the resources on either site. The flag for Reverse mappings is available mapping is easier to configure with once click for both sites.
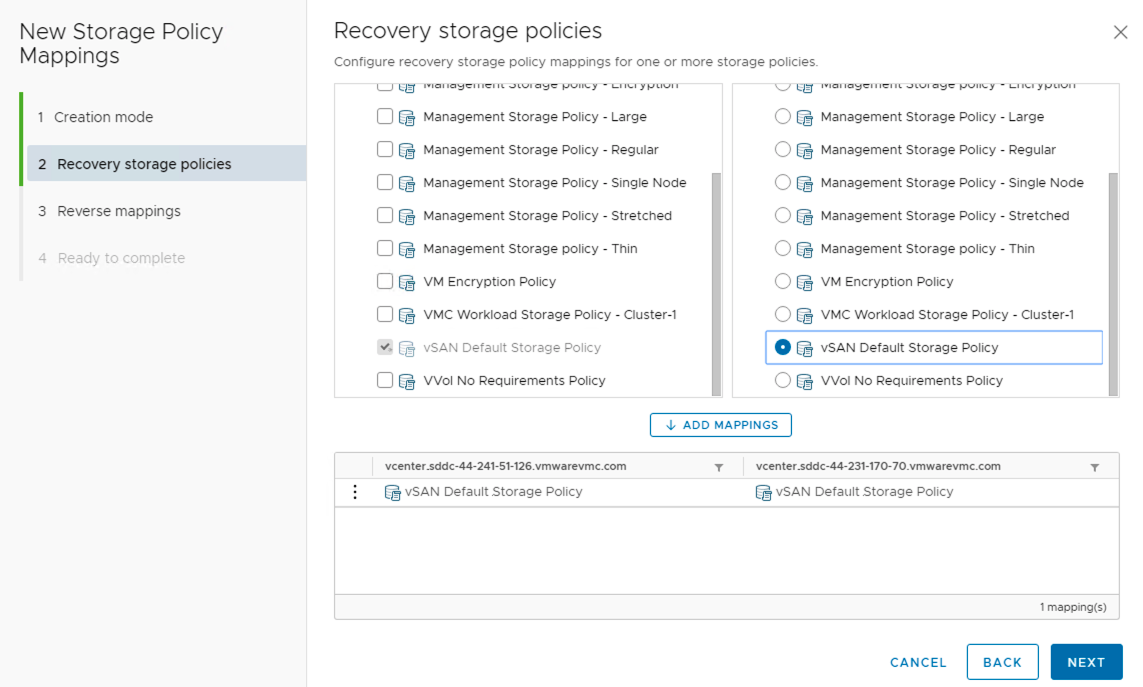
Storage Policy Mapping
Since the supported storage on VMware Cloud on AWS is vSAN, we also need to perform Storage Policy Mappings. Mapping creations can be automatic (based on names) or manual. Additional flags included along with mapping is Reverse Mapping.
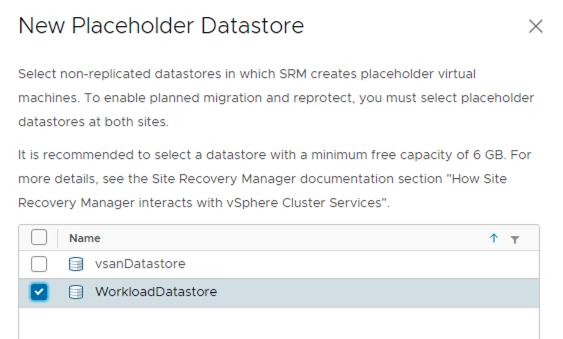
Placeholder Datastores
A placeholder virtual machine is a subset of virtual machine files. Site Recovery Manager uses that subset of files to register a virtual machine with vCenter Server on the recovery site.
The files of the placeholder virtual machines are very small, and do not represent full copies of the protected virtual machines. The placeholder virtual machine does not have any disks attached to it. The placeholder virtual machine reserves compute resources on the recovery site, and provides the location in the vCenter Server inventory to which the protected virtual machine recovers when you run recovery.
The presence of placeholder virtual machines on the recovery site inventory provides a visual indication to vCenter Server administrators that the virtual machines are protected by Site Recovery Manager. The placeholders also indicate to vCenter Server administrators that the virtual machines can power on and start consuming local resources when Site Recovery Manager runs tests or runs a recovery plan.
When you recover a protected virtual machine by testing or running a recovery plan, Site Recovery Manager replaces the placeholder with the recovered virtual machine and powers it on according to the settings of the recovery plan. After a recovery plan test is executed/completed, Site Recovery Manager restores the placeholders and powers off the recovered virtual machines as part of the clean up process.
This is per vCenter configuration which must be configured by clicking on each tab.
Creating Protection Groups
A protection group is a collection of virtual machines that the Site Recovery Manager protects together. Protection group are per SDDC configuration and needs to be created on each SDDC if VMs are replicated in bi-directionally.
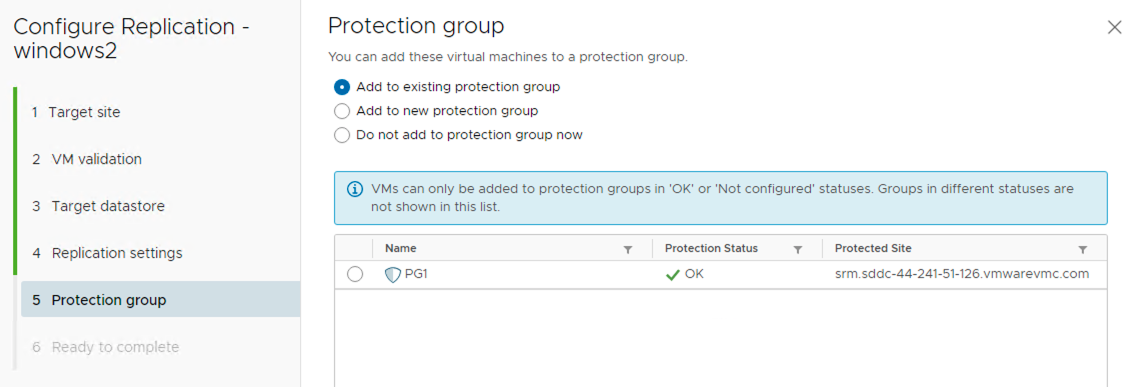
There are two ways to connect a VM to the protection group.
- Add a VM to the existing protection group while enabling vSphere replication on the virtual machine.
2. Virtual machines in the vCenter Server inventory that are configured for replication are available for selection when you create or edit the protection group.
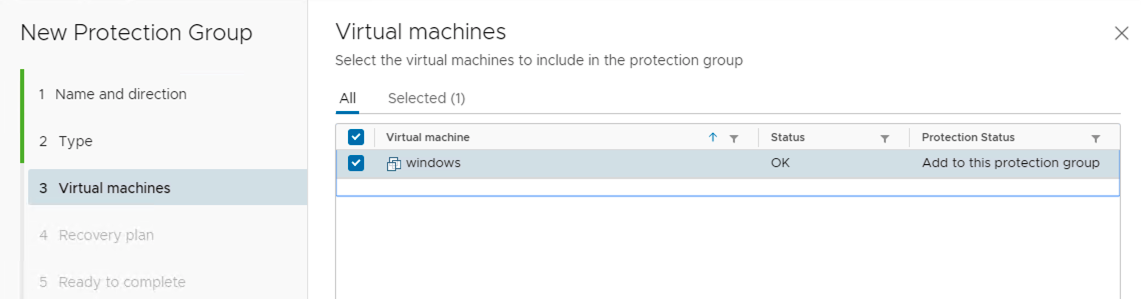
When using vSphere Replication protection groups, Site Recovery Manager is dependent on vSphere Replication, but vSphere Replication is not dependent on Site Recovery Manager. You can use vSphere Replication independently of Site Recovery Manager. For example, you can use vSphere Replication to replicate all the virtual machines in the vCenter Server inventory, but only include a subset of those virtual machines in protection groups. Changes that you make to vSphere Replication configuration can affect the Site Recovery Manager protection of the virtual machines that you do include in protection groups.
Site Recovery Manager monitors the vSphere Replication status of the virtual machines in vSphere Replication protection groups. If replication is not functioning for a virtual machine in a protection group, Site Recovery Manager cannot recover the virtual machine.
If you unconfigure vSphere Replication on a virtual machine, Site Recovery Manager continues to include that virtual machine in protection groups in which you included it. Site Recovery Manager cannot recover that virtual machine until you reconfigure replication. If you unconfigure vSphere Replication on a virtual machine, you have to remove it from the protection group manually.
If you remove a virtual machine with vSphere Replication from a protection group, vSphere Replication continues to replicate the virtual machine to the recovery site. The virtual machine does not recover with the rest of the virtual machines in the protection group if you run an associated recovery plan.
Recovery Plan
A recovery plan is like an automated runbook. It controls every step of the recovery process, including the order in which Site Recovery Manager powers on and powers off virtual machines, the network addresses that recovered virtual machines use, and so on. Recovery plans are flexible and customizable.
A recovery plan runs a series of steps that must be performed in a specific order for a given workflow such as a planned migration or reprotection. You cannot change the order or purpose of the steps, but you can insert your own steps that display messages and run commands.
A recovery plan includes one or more protection groups. Conversely, you can include a protection group in more than one recovery plan. For example, you can create one recovery plan to handle a planned migration of services from the protected site to the recovery site for the whole SDDC and another set of plans per individual departments. Thus, having multiple recovery plans referencing one protection group allows you to decide how to perform recovery.
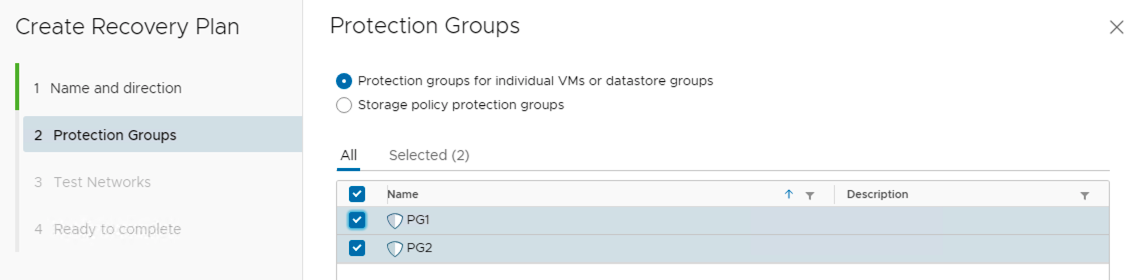
You can run only one recovery plan at a time to recover a particular protection group. If you test or run a recovery plan with a protection group that is shared in other recovery plans, the other recovery plans change the state of the protection group to “protectionGroup In Use” and you cannot run them.
Site Recovery Manager runs the recovery plan steps in different ways depending on the configuration.
- Runs some of the steps during all recoveries
- Runs some of the steps only during test recoveries
- Some of the steps are always skipped during test recoveries
Similar to protection groups, recovery plans are also SDDC- specific and must be created on each SDDC, if replication is configured bi-directionally.
You can configure a recovery plan to perform many actions/tasks:
- Run commands on a virtual machine
- Display messages that require a response when the plan runs on the Site Recovery Manager Server or in the guest OS
- Suspend non-essential virtual machines during recovery
- Configure dependencies between virtual machines
- Customize virtual machine network settings
- Change the recovery priority of protected virtual machines.
You can add pre or post-scripts to a VM’s recovery plan and configure the execution of the plan in a few different ways:
- Execute recovery steps to completion
- Wait for user inputs at specific points in the process
- Stop and wait for a specified time limit, continue, stop again and then complete the plan.
Recovery Order
When you run a recovery plan, Site Recovery Manager performs the following operations:
- Powers off the virtual machines according to the priority that you set, with high-priority virtual machines powering off last. Site Recovery Manager skips this step when you test a recovery plan.
- Powers on groups of virtual machines on the recovery site according to the priority that you set. Before a priority group starts, all the virtual machines in the next-higher priority group must recover or fail to recover.
During recovery, dependencies between virtual machines within different priority groups are ignored. If dependencies exist between virtual machines in the same priority group, Site Recovery Manager first powers on the virtual machines on which other virtual machines depend on.
If Site Recovery Manager can meet the virtual machine dependencies, it attempts to power on as many virtual machines in parallel as vCenter Server supports.
VM Recovery Properties
A replicated VM configured under a Recovery plan provides the following recovery options.
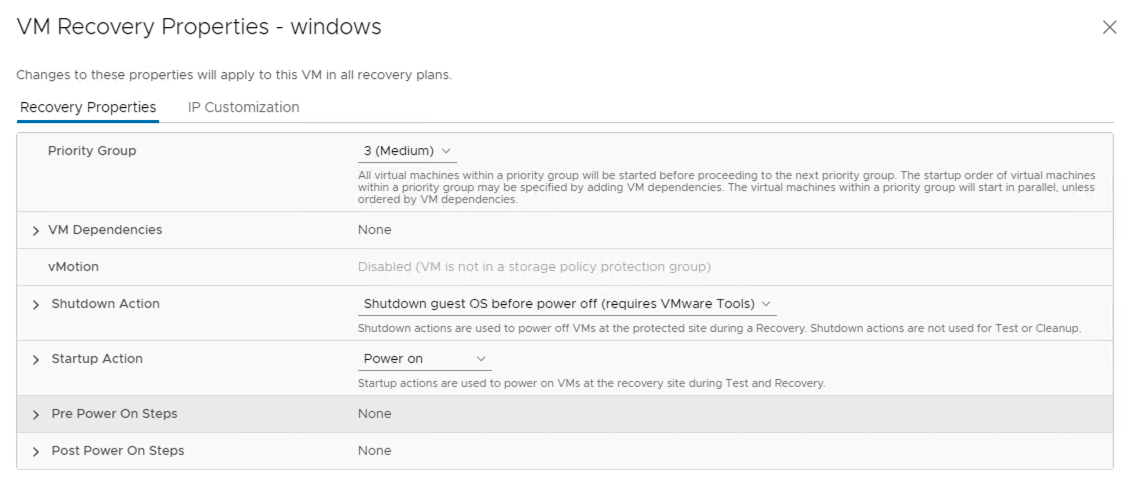
Priority
Site Recovery Manager starts virtual machines on the recovery site according to the priority that you set. The recovery priority determines the shutdown and power-on order of virtual machines.
By default, Site Recovery Manager sets all virtual machines in a new recovery plan to recovery priority level 3. You can increase or decrease the recovery priority of a virtual machine. If you change the priority of a virtual machine, Site Recovery Manager applies the new priority to all recovery plans that contain this virtual machine.
Site Recovery Manager starts the priority 1 virtual machines first, then priority 2 virtual machines second, and so on. Site Recovery Manager uses VMware Tools heartbeat to discover when a virtual machine is running on the recovery site. In this way, it can ensure that all virtual machines of a given priority are running before it starts the virtual machines of the next priority.
VM Dependencies
If a virtual machine depends on services that run on another virtual machine in the same protection group, you can configure a dependency between the virtual machines. By configuring a dependency, you can ensure that the virtual machines start on the recovery site in the correct order. Dependencies are only valid if the virtual machines have the same priority.
When a recovery plan runs, Site Recovery Manager starts the virtual machines that other virtual machines depend on before it starts the virtual machines with the dependencies. If Site Recovery Manager cannot start a virtual machine that another virtual machine depends on, the recovery plan continues with a warning. You can only configure dependencies between virtual machines that are in the same recovery priority group. If you configure a virtual machine to be dependent on a virtual machine that is in a lower priority group, Site Recovery Manager overrides the dependency and first starts the virtual machine that is in the higher priority group.
If you remove a protection group that contains the dependent virtual machine from the recovery plan, the status of the protection group is set toNot in this Plan in the dependencies for the virtual machine with the dependency. If the configured virtual machine has a different priority than the virtual machine that it depends on, the status of the dependent virtual machine is set to Lower Priority or Higher Priority.
Shutdown and Startup actions
You can configure how a virtual machine starts up and shuts down on the recovery site during a recovery.
You can configure whether to shut down the guest operating system of a virtual machine before it powers off on the protected site. You can configure whether to power on a virtual machine on the recovery site. You can also configure delays after powering on a virtual machine to allow VMware Tools or other applications to start on the recovered virtual machine before the recovery plan continues.
Recovery Plan Timeouts and Pauses
Several types of timeouts can be configured during the running of recovery plan steps. Timeouts cause the plan to pause for a specified interval to allow the step time to finish. This is configurable using the pre and post-power-on steps.
Message steps force the plan to pause until the user acknowledges the message. Before you add a message step to a recovery plan, ensure that the message is necessary.
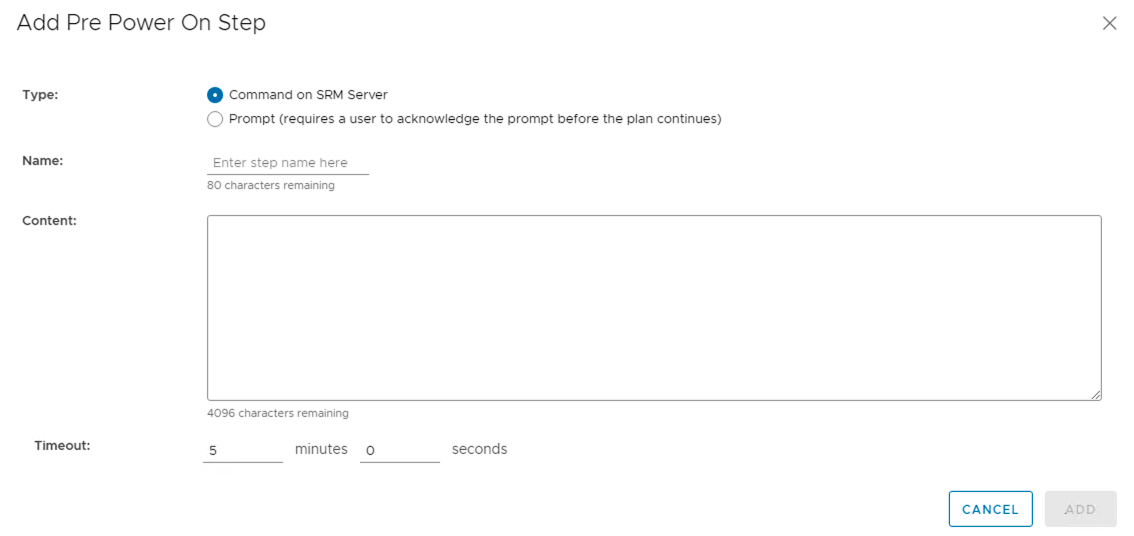
An additional option in post power on steps is to run a command on the recovered VM.

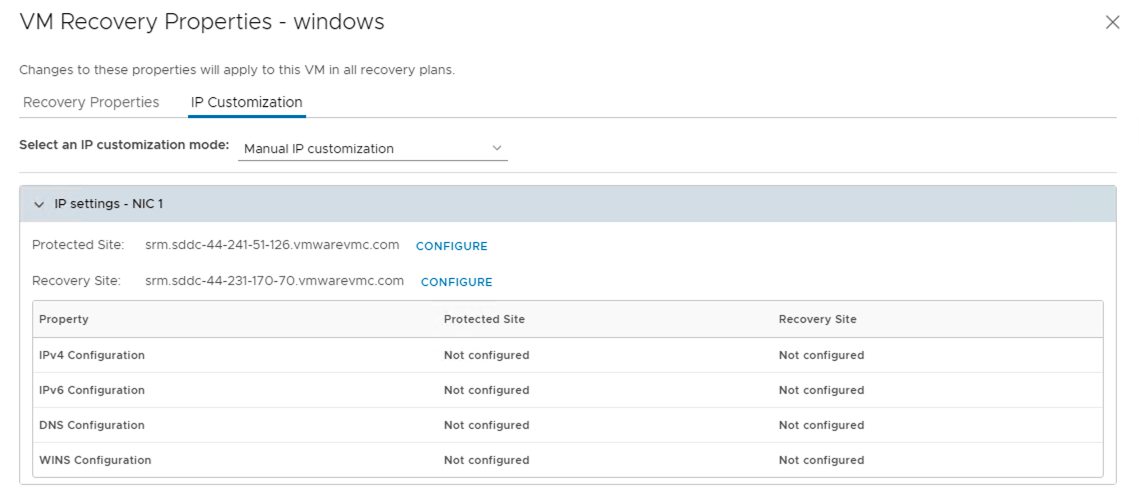
IP Customization
As mentioned in the earlier section in this document, you can customize IP settings for virtual machines for the protected site and the recovery site. Customizing the IP properties of a virtual machine overrides the default IP settings when the recovered virtual machine starts at the destination site.
If you do not customize the IP properties of a virtual machine, Site Recovery Manager uses the IP settings for the recovery site during recovery or a test from the protection site to the recovery site. Site Recovery Manager uses the IP settings for the protection site after reprotect during the recovery or a test from the original recovery site to the original protection site.
Site Recovery Manager supports different types of IP customization.
- Use IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
- Configure different IP customizations for each site.
- Use DHCP, Static IPv4, or Static IPv6 addresses.
- Customize addresses of Windows and Linux virtual machines.
- Customize multiple NICs for each virtual machine.
Note: You only configure one IP address per NIC.

Additionally, VMware Cloud on AWS also enables use of DR IP Customizer Tool for IP customization of virtual machines.
The DR IP Customizer tool allows you to define explicit IP customization settings for multiple protected virtual machines on the protected and recovery sites.
In addition to defining subnet IP mapping rules, you can use the DR IP Customizer tool to apply customized networking settings to virtual machines when they start on the recovery site. For Syntax, structure, and detailed information please refer to product documentation here.
Testing a Recovery Plan
When you create or modify a recovery plan, test it before you try to use it for planned migration or for disaster recovery.
By testing a recovery plan, you ensure that the virtual machines that the plan protects recover correctly to the recovery site. If you do not test recovery plans, an actual disaster recovery situation might not recover all virtual machines, resulting in data loss.
Testing a recovery plan exercises nearly every aspect of a recovery plan, although Site Recovery Manager makes several concessions to avoid disrupting ongoing operations on the protected and recovery sites. Recovery plans that suspend local virtual machines do so for tests and for actual recoveries. With this exception, running a test recovery does not disrupt replication or ongoing activities at either site.
If you use vSphere Replication, when you test a recovery plan, the virtual machine on the protected site can still synchronize with the replica virtual machine disk files on the recovery site. The vSphere Replication Server creates redo logs on the virtual machine disk files on the recovery site, so that synchronization can continue normally. When you perform a clean-up after running a test, the vSphere Replication Server removes the redo logs from the disks on the recovery site and persists the changes accumulated in the logs to the VM disks.
You can run test recoveries as often as necessary and can cancel a recovery plan test at any time.
Reprotect
After Site Recovery Manager performs a recovery, the virtual machine's start-up on the recovery site. By running reprotect when the protected site comes back online, you reverse the direction of replication to protect the recovered virtual machines on the recovery site back to the original protected site.
Reprotect uses the protection information that you established before a recovery to reverse the direction of protection. You can initiate the reprotect process only after recovery finishes without any errors. If the recovery finishes with errors, you must fix all errors and rerun the recovery, repeating this process until no errors occur.
You can conduct tests after a reprotect operation completes, to confirm that the new configuration of the protected and recovery sites is valid.
Before performing the reprotect process, note the following:
- You performed a recovery either as part of a planned migration or as part of disaster recovery.
- The original protected site is running.
- You have not run reprotect since the recovery.
- If you performed a disaster recovery, you must perform a planned migration when the hosts and datastores on the original protected site are running again.
Proceed with reprotect only if you meet the above criteria. The reprotect reverses the replication path from the DR site to the production site and then runs the recovery of VMs from the DR site to the production site. In case of any failure during this recovery, you will have an option to do force cleanup.
Note - Force cleanup is only available after you run reprotect once and errors occur. Enabling this option forces the removal of virtual machines, ignore errors, and returns the recovery plan to the ready state.
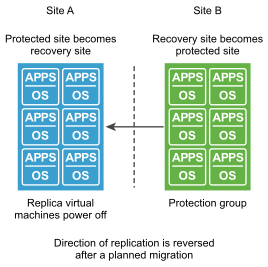
Reprotect results in the reconfiguration of Site Recovery Manager protection groups and recovery plans to work in the opposite direction. After a reprotect operation, you can recover virtual machines back to the original site using a planned migration workflow.
When the planned migration completes, the virtual machines are running on the original protected site but the virtual machines are not protected. The virtual machines on the original recovery site (DR site), are powered off. You must perform a second reprotect operation to start the replication now from the production site to the DR site.
Reports
Site Recovery Manager history reports are useful to diagnose the Site Recovery Manager Server behavior before and after a failure. You can change the number of historical reports to export.
You can view and export reports about each run of a recovery plan, test recovery plan, test cleanup, or perform reprotect.
Recovery plan histories provide information about each run, test, clean up, or reprotect of a recovery plan. The history contains information about the result and the start and end times for the whole plan and for each step in the plan. You can export history at any time, but history always contains entries only for completed operations. If an operation is in progress, the history appears after the operation completes.
Site Recovery Manager preserves history for deleted recovery plans. You can export history reports for existing and deleted plans.
