Protection Groups and Recovery Plans (VCDR)
Create a Protection Group
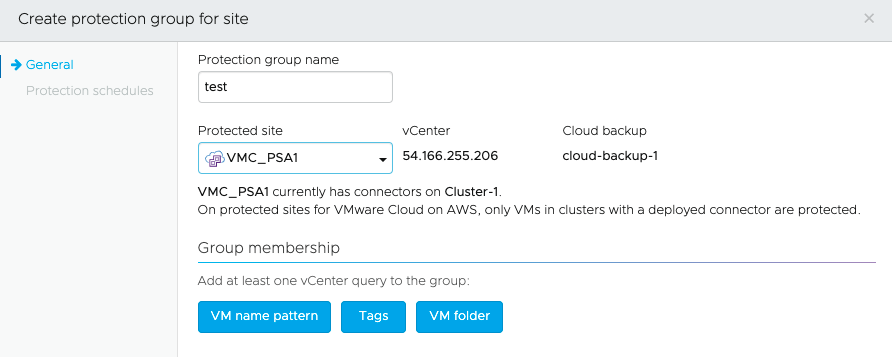
A protection group means that you create and group a set of VMs which can be then used for recovery. You can create multiple groups of VMs. VMs that are a part of a Protection group should exist on the same protected site only. Creation of protection group needs an existing subscription.
- Choose the protected site and vCenter from which the VMs will be selected.
- Create vCenter queries that define the protection group's dynamic membership. A vCenter query is defined using vSphere tags, folders, and/or VM name patterns. These vCenter queries are evaluated each time a snapshot is taken and define the contents of the snapshot.
- Define how frequently you want to take snapshots of the VMs defined in the group using a snapshot schedule. You also define how long you want to retain those snapshots on the SCFS.
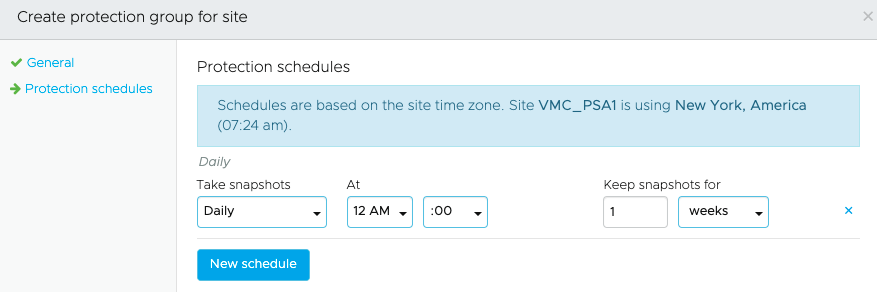
Important: Research indicates most victims of ransomware do not discover that they have been compromised until an average of 3-6 months after the initial infection, so choose the retention period accordingly.
Create a Disaster Recovery Plan
A DR plan defines the orchestration configuration for disaster recovery and workload mobility.
You can create, name, edit, duplicate, save, and run DR Plans. Environment variables in a plan map difference between the sites for smooth recovery, ensuring that vSphere configurations and parameters are mapped consistently between sites.
Plans run either for recovery as an actual DR operation, or they run as a test recovery, which performs all the plan’s recovery operations in a test site for validation.
The following operations are allowed under the DR plan section:
- Configuring DR Plans - require defining where you want your protected data moved to when the plan runs.
- Viewing DR Plans - shows the currently defined plans along with plan summary information: the current status, protected and recovery sites, and the last run compliance check results.
- Activating DR Plans - can be in an active or deactivated state.
Configuring a DR Plan for On-demand Use Case
Configuring DR plans require defining where you want to move your protected data when the plan runs.
Specifically, your plan must define where the protected resources such as protection groups, VMs, files, vCenter(s), all vCenter folders, compute resources, virtual networks, and IP addresses (individual or ranges) are moved to on the recovery site.
Follow the steps below to configure alerts and recovery steps In the VCDR UI:
- Create a DR plan and choose Recovery Site for Failover. For this use case choose Recovery SDDC deployed in case of disaster.
- Choose the Protected site (in case you have more than one, choose the site where the protection group is created).
- Choose the protection group which would be failed over when this DR plan is executed.
- Choose a location to save the custom scripts.
- Add recovery steps. There are different options under the Recovery Steps.
- Choose a step which can be executed for either whole protection groups or an individual VM under the protection group.
- Select the power action for recovered VMs.
- Select pre-recover or post-recover actions from the drop-down menu which can be running scripts which were saved under step 4 above.

- Configure alerts. Ensure you have added recipients for alerts.

Configuring a Disaster Recovery Plan for Pilot Light
Configuring DR plans require defining where you want your protected data moved to when the plan runs.
Specifically, your plan must define where protected resources are moved to on the recovery site: protection groups, VMs, files, vCenter(s), all vCenter folders, compute resources, virtual networks, and IP addresses (individual or ranges).
Additionally, you must configure the Test Site operating environment for failover exercises.
- Create a DR plan and choose Recovery Site for Failover. For this configuration, choose Existing Recovery SDDC.
- Choose the Protected site (if there is more than site, choose the site where the PG is created).
- Choose the Protection group which would be failed over when this DR plan is executed.
- Perform Mapping for vCenter, Folders, Compute, network and IP between the sites. An option flag is provided for each of these options if the mappings are same for test and failover.
- Perform protected and recovery site vCenter Mapping.
- Map each vCenter folder in 'Protected Site' containing protected VMs to a folder in 'Recovery SDDC'.
- Map each vCenter compute resource in 'Protected Site' containing protected VMs to a compute resource in 'Recovery SDDC'
- Map each vCenter virtual network in 'Protected Site' containing protected VMs to a virtual network in 'Recovery SDDC'
- Map source subnets to subnets in Recovery SDDC
- The script VM is where the custom scripts specified in the recovery steps are run. Both Windows and Linux are supported; the VM must have VMware Tools installed. When running the plan, you will need to enter the credentials to run the scripts.
- Add recovery steps. There are different configurable option under the Recovery Steps.
- Choose the type of execution of step which can be but not limited to whole Protection groups or a few individual VM under the protection group.
- Power action for recovered VMs.
- Pre-recover or Post-recover actions which can be running scripts which were saved under step 4 above.
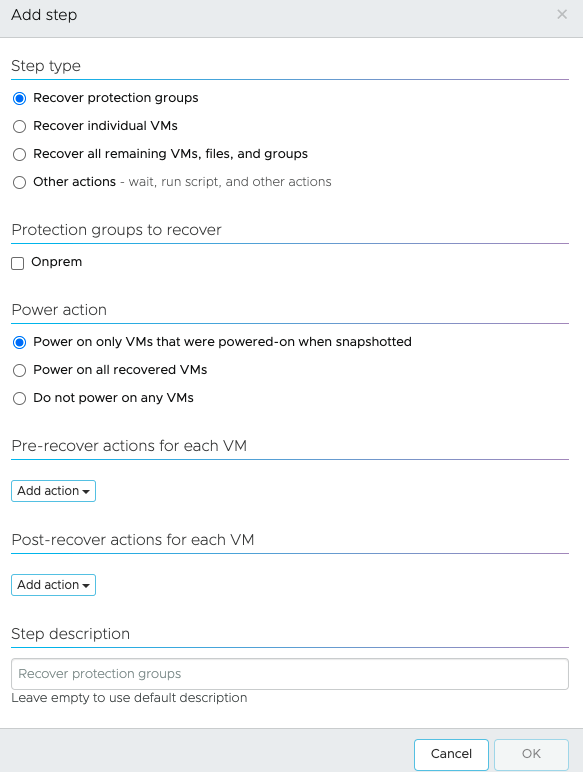
- Configure alerts. Ensure to add recipients for alerts.
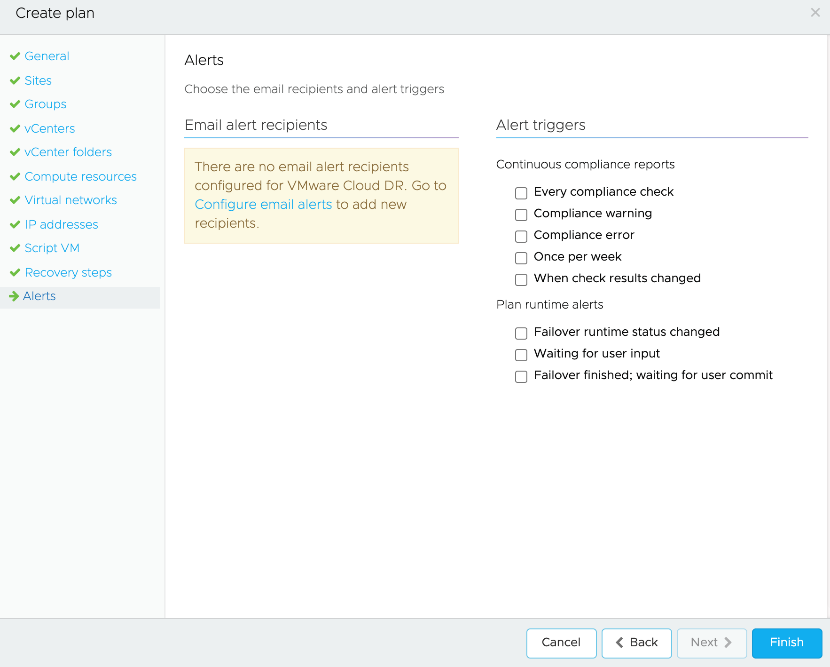
Executing a Disaster Recovery Plan
Now that you have created a DR plan, take a look at these additional options.
- DR plan status
- Compliance checks status
- Executing a test plan
- Perform a failover
- Reports
Status of DR plan
Each DR plan protects a single vSphere protected site. The status of DR plans are different when created for On-demand and Pilot Light deployments. The On-Demand deployment will show the status No recovery site' which is expected. At this moment there is no automated option of running a test recovery for an on-demand use case unless the recovery SDDC is deployed. You can also choose to have the DR plan in activated or a deactivated state when the status of the DR plan is Ready.
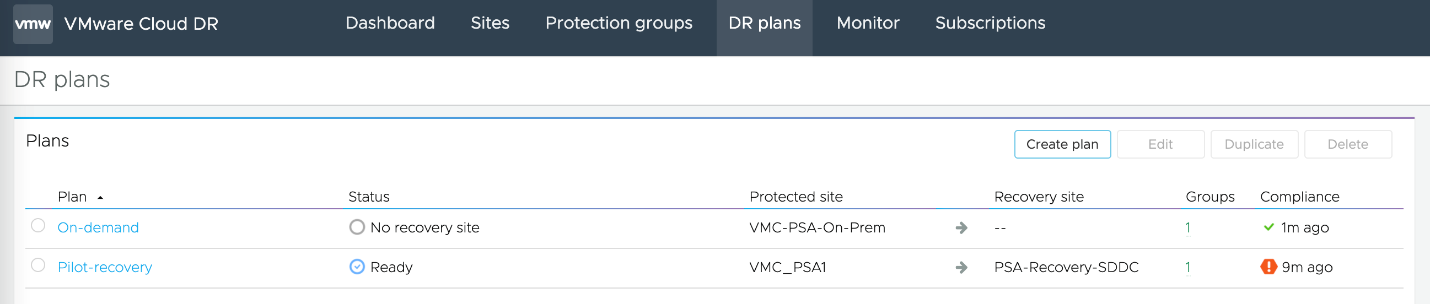
When configuring a recovery site for On-demand DR plan you need to perform similar mapping as done for Pilot light which includes vCenter, Compute, Folder, Networks and IP address. You also need to specify the Script VM configuration.
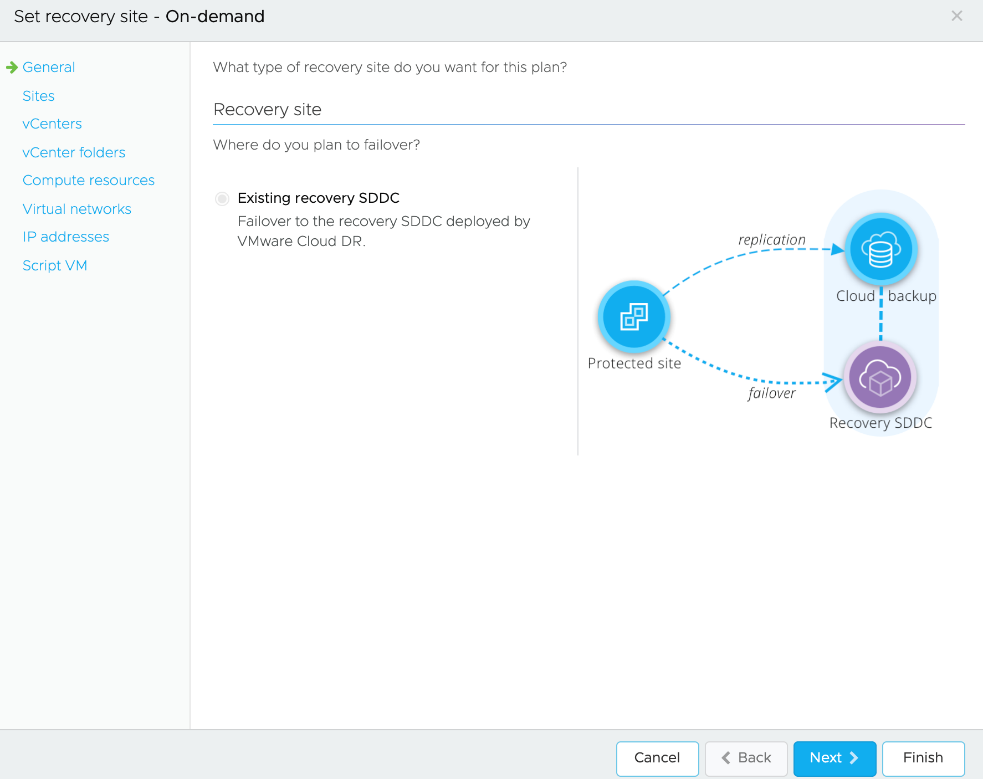
The Pilot-Recovery DR plan status is 'Ready' since the recovery site configuration and mapping of resource is a mandate when creating one.
There are additional states in a DR plan. For more details about these different states, see VCDR document.
Compliance Checks Status
Continuous compliance checks verify the integrity of a DR plan and ensure that any changes in the failover environment do not invalidate a DR Plan’s directives when running.
Compliance checks also make sure that the specified protection groups are live on the protected site and are replicating successfully to the target Recovery SDDC. Compliance checks run automatically every 30 minutes for activated plans. A plan can become out of compliance if any of its conditions become violated because of environmental or plan configuration changes. An example is in below screenshot.

Executing a Test Plan
A test failover runs in the context of its own test failover environment, specified by the DR plan’s test mapping rules. The results of the test failover do not permanently affect a target failover destination.
You can choose the snapshot state to be used to run the test recovery. A test failover stops on the first failure by default. You can override all other default behavior using custom options.
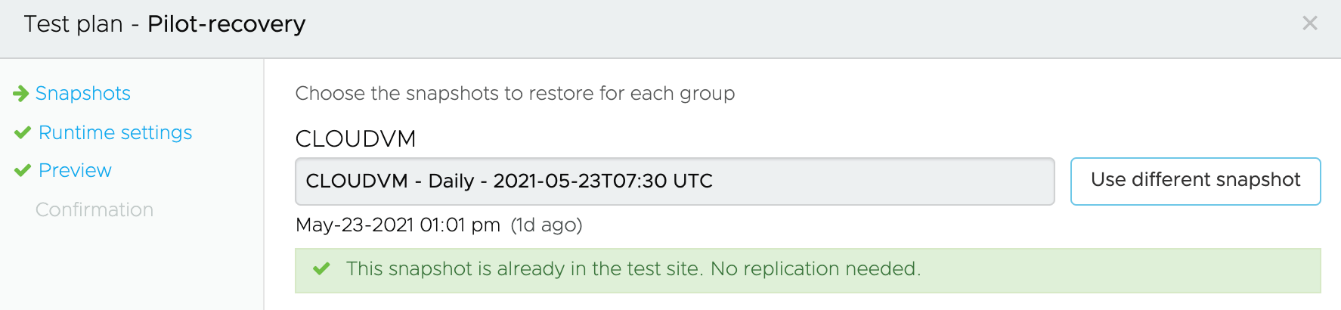
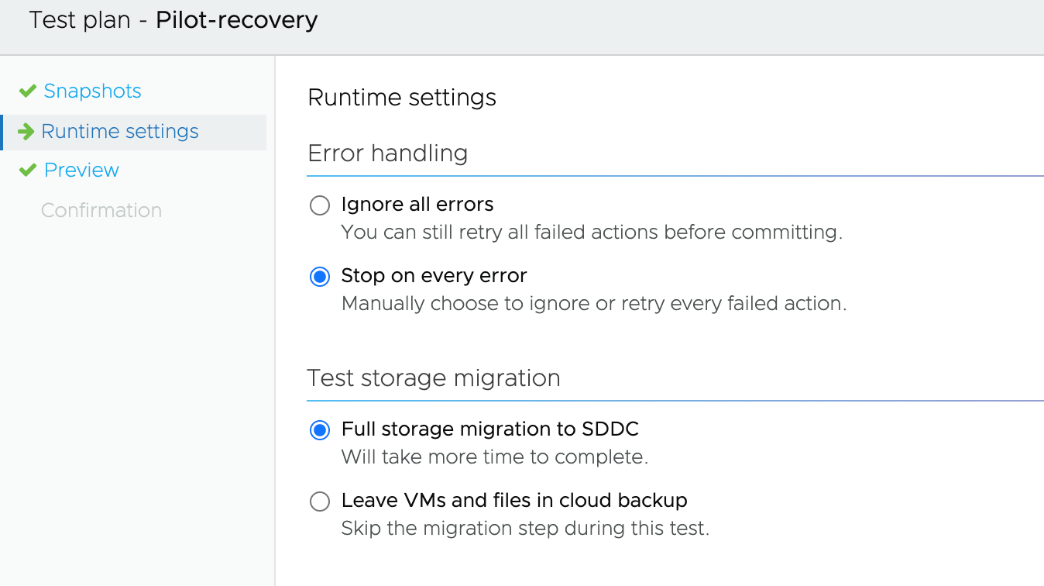
Test failover operations give you the option of performing a full storage vMotion from the staging datastore to the SDDC datastore to emulate a real failover, or to leave VMs on the staging datastore to cut down on the failover time (preview feature), and to allow you to test and debug your failover faster. This preview feature is available in Test Failover only at this time.
Note that a svMotion(All test recovered VM’s) task during a test failover must complete in order to initiate a cleanup. The time taken for this Storage vmotion task is dependent on the how large are the disk attached to the VM’s.
The following steps are executed when you choose the Test storage migration to leave the VMs and files in cloud backup. Note that there is no relocate virtual machine task executed.
Perform a failover
First wizard when performing a failover is summary of compliance check. This is in place to ensure that compliance information is validated before execution. You also get to choose the snapshot available from the DR plan which needs to be used during failover.
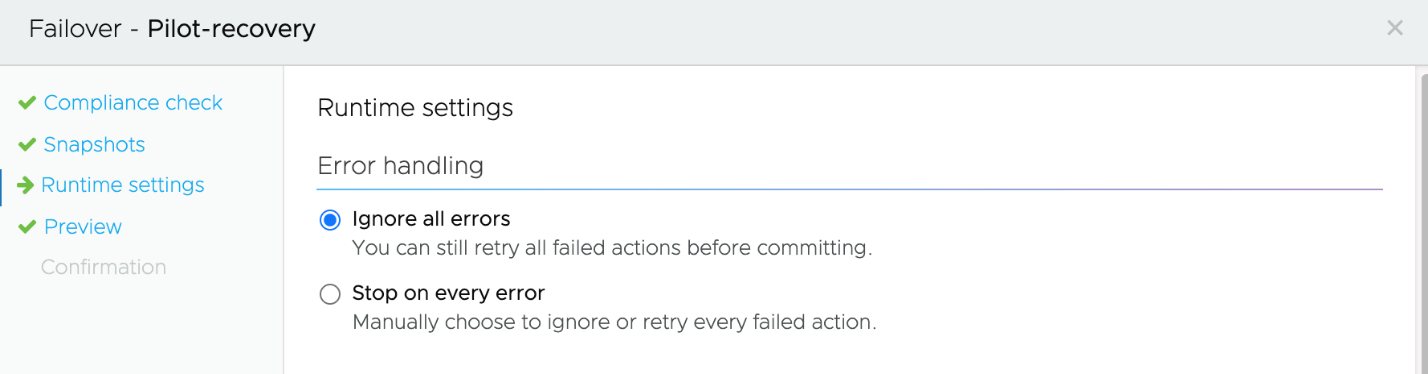
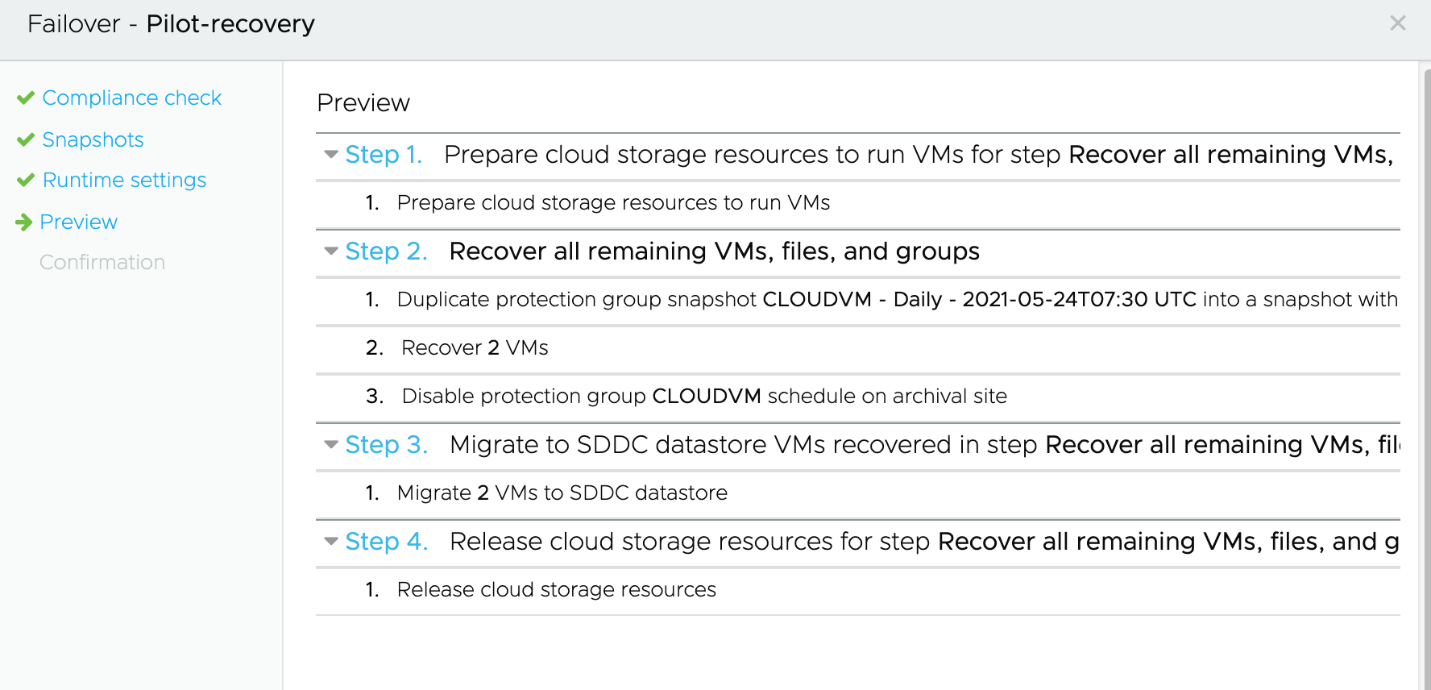
The Runtime is default at Ignore all error by default and the preview would help understand the steps which would be executed. When it begins running, the plan moves into the failover state. You can observe the running plan’s progress from the plan’s detail page.
You can also observe the storage VMotion from the Staging datastore to the SDDC datastore following VM recovery
While a plan runs, you can perform the following operations:
- Cancel/Cancel and Rollback
- Wait for user input
- Terminate
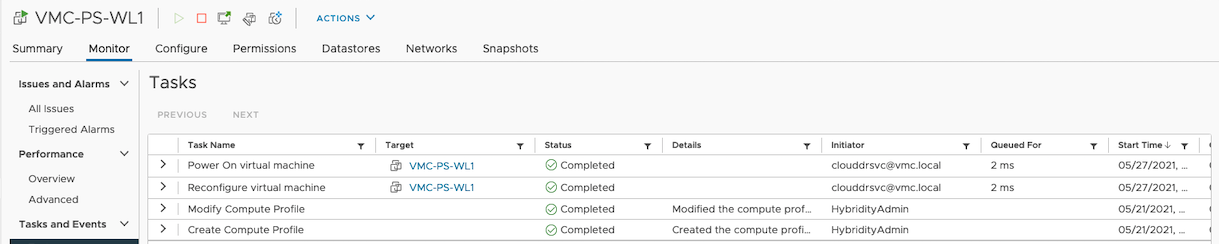
Note the events on the VM which is chosen for failover. The VM is relocated to the WorkloadDatastore of the SDDC from the Cloud backup location mounted as ds01 over NFS.
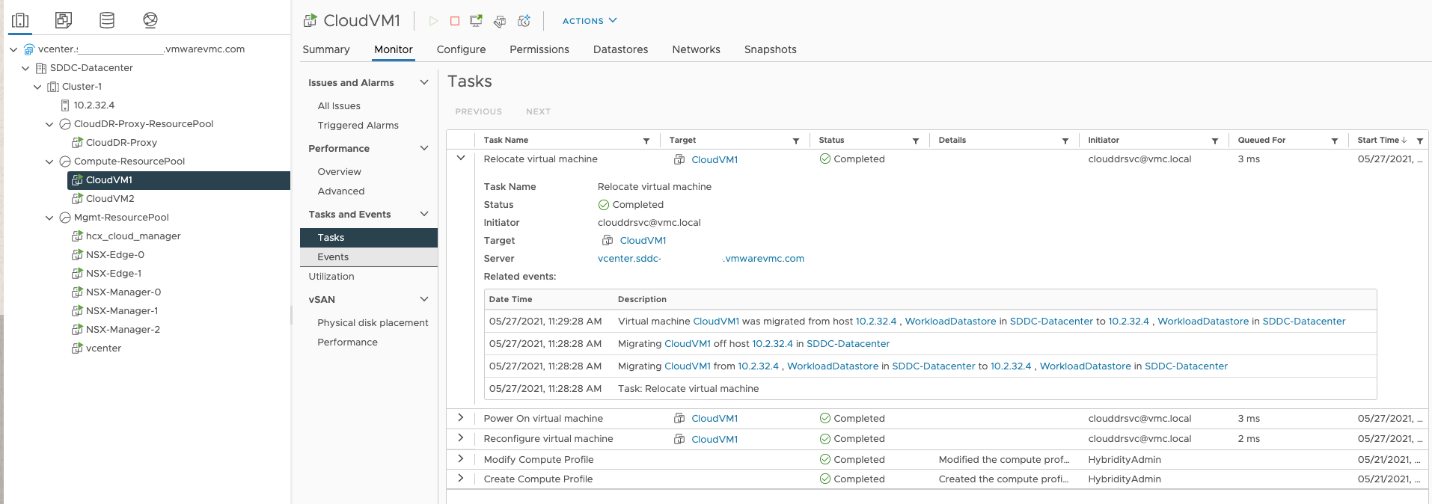
Failback to the Primary Site
After a failback is executed , you can replicate the data from the VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC to the protected site. A failback from VMware Cloud on AWS includes the following sequence of steps:
- VMs are powered off on the SDDC.
- A last VM snapshot is taken following the power off. The differences between the VM state at the time of recovery and failback are then applied to the snapshot used for recovery to construct a VM backup on the SCFS for subsequent retrieval.
- These VM backups are then retrieved to an on-premises system using a general forever incremental protocol.
- VMs are recovered to a protected vSphere site.
- Upon successful recovery, VMs are automatically deleted from the SDDC.
- Option to create a failback plan when committing a failover is provided thus reducing the overhead for creating a DR plan manually.
You must configure the default datastore for recovery VM. This is useful when you choose to restore VMs back to different location than the earlier VM. This location can be a datastore in an existing protected site or a new datastore in a new protected site.
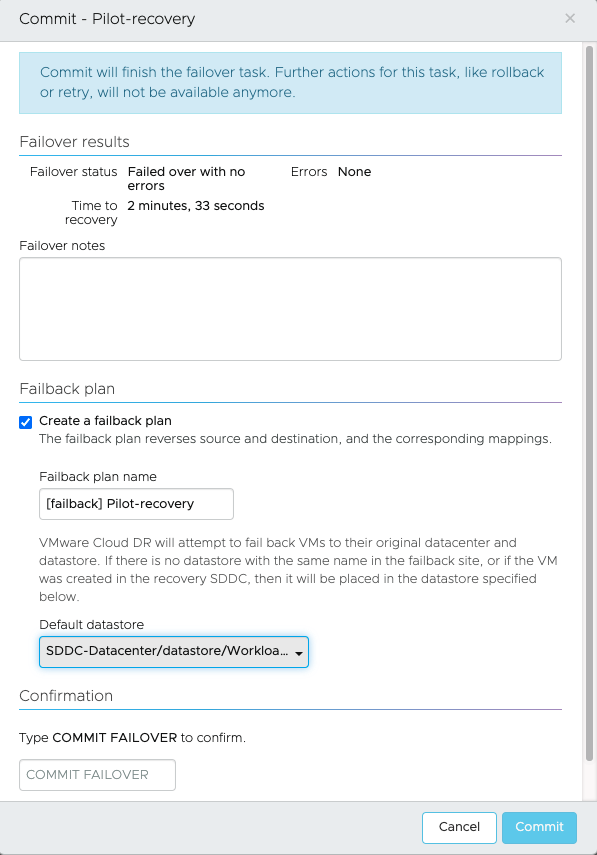
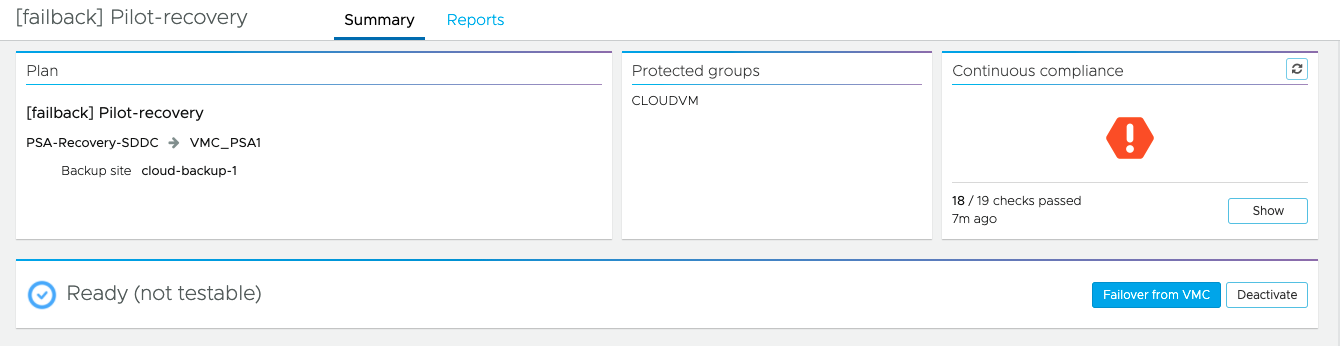
Failback from an SDDC returns only changed data. There is no rehydration, and the data remains in its native compressed and deduplicated form. You have to activate the plan which is created to run the failback.

Once the plan is activated, you get an option to failover from the VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC:
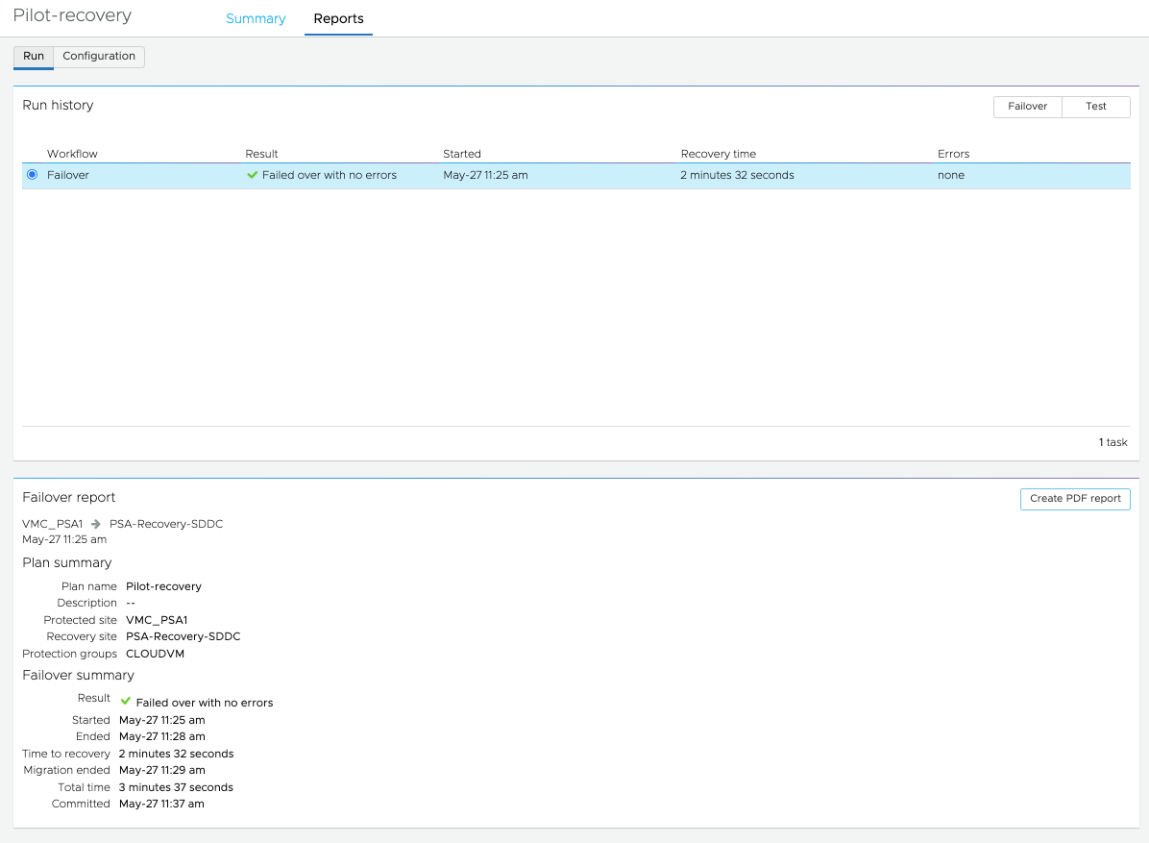
Reports
Failover and test failover reports provide information about a completed DR plan operation.
After a failover or test failover plan has completed (and you have committed or acknowledged the plan), you can generate a PDF report of the plan operation by clicking the Reports tab on a plan’s details page.
The generated report contains summaries of the plan configuration at the time of recovery, and a summary of the recovery. The report also includes details for the recovery mappings, the plan’s recovery steps, and a detailed report on each action taken during the recovery operation, and any errors that occurred.