Feature Brief: Compute Policies
Introduction
Compute policies provide a way to specify how the vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) should place VMs on hosts in a resource pool.
The compute policies for VMware Cloud on AWS are
• VM-Host Affinity Policy – For when a category of VMs must run on a specific category of hosts. Helpful if you want some VMs to run on hosts with a specific set of characteristics.
• VM-Host Anti-Affinity Policy – For when a category of VMs must not run on a specific category of hosts.
• VM-VM Affinity Policy – For when you want a category of VMs to run on the same host to minimize latency between the VMs, or for when you want to keep specific VMs together
to simplify auditing.
• VM-VM Anti-Affinity Policy – For when you do not want a category of VMs to run on the same host. For example, if you have highly available workloads and you want to ensure that the loss of a host cannot bring down your applications.
• Disable-DRSvMotionPolicy–For when you have workloads on which you prefer DRS not to use vSphere vMotion. This type of policy keeps a VM on a specific host as long as that host is available. Useful in conjunction with VM-VM affinity rules.
In VMware Cloud on AWS, compute policies are always defined for the entire SDDC, not only for a single cluster. However, VMs are only moved within the cluster in which they were originally started. DRS will not move a VM from one cluster to another.
Important Consideration
These policies do not take effect in certain situations; for example,
• The rules cannot prevent a VM from being powered on, and if no available hosts match the policy, the VM is placed on any available host
• The rules cannot prevent a host from entering maintenance mode, or from executing a failover.
• The rules cannot prevent a VM from being manually placed on a specified host, but the rules correct the VM placement according to the policy at the next remediation cycle
The system does not check for policy conflicts. If, for example, multiple VMs subject to the same VM-Host affinity policy are also subject to a VM-VM anti-affinity policy, DRS will be unable to place the VMs in a way that complies with both policies. If it's not possible to place a VM on a host that satisfies the policy, DRS attempts to place the VM on any suitable host.
Given these limitations, compute policies should not be used in cases where strict adherence to affinity rules is required. For example, they cannot guarantee that an application will run only on a subset of hosts in a cluster for licensing purposes. Instead, it is recommended to create a separate cluster, and then license all the hosts in the cluster, plus one more host for maintenance purposes, to run the application. DRS will move the application within the cluster, but will never move it to another cluster.
Creating and Applying Policies
To create a compute policy, log in to your VMware Cloud on AWS console. Select your SDDC
and click Open vCenter to launch the vSphere Client. Select Menu > Policies and Profiles.
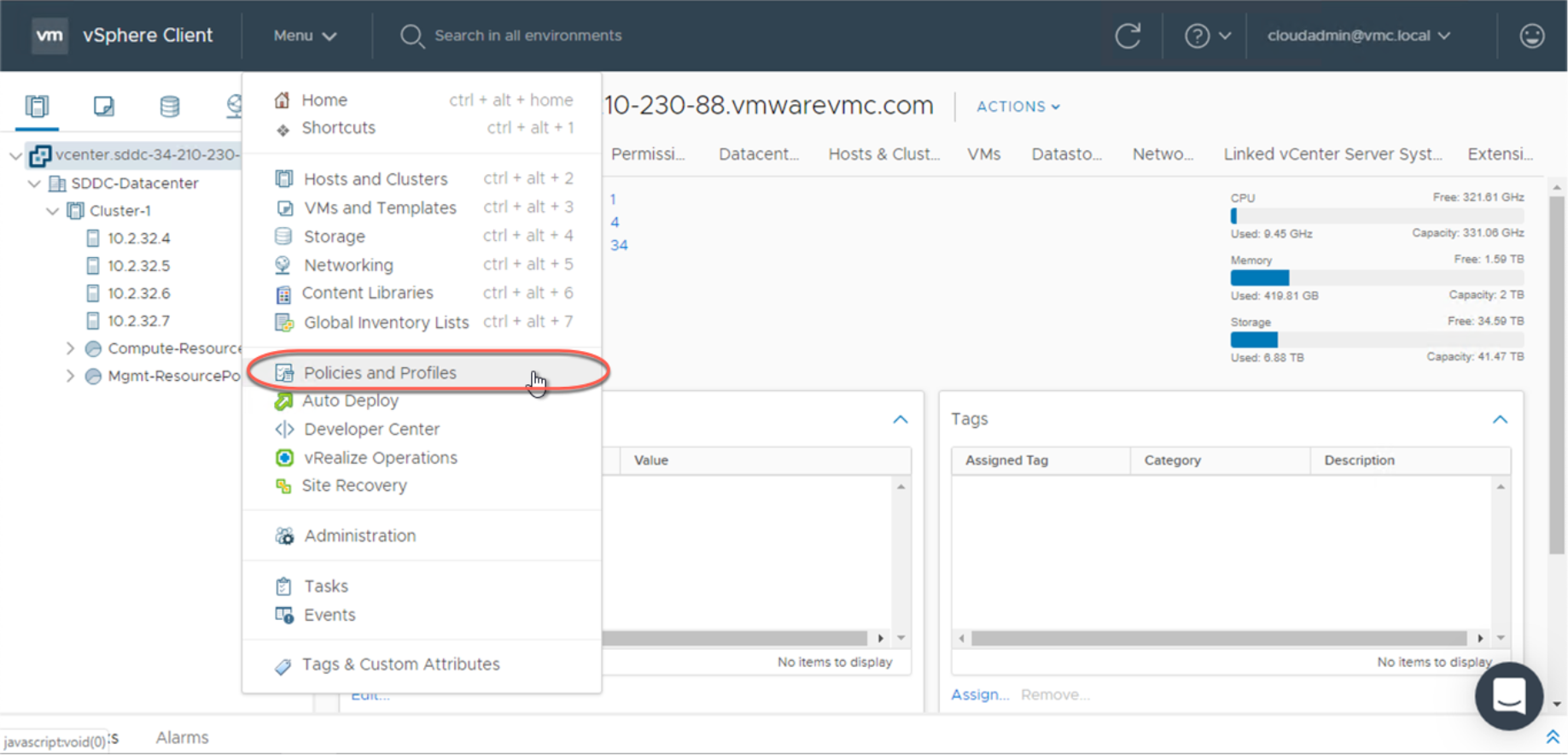
From the left column, click Compute Policies, then click Add to open the New Compute Policy wizard. In the wizard, specify the
• Type of policy
• Policy name
• Description
• Tag
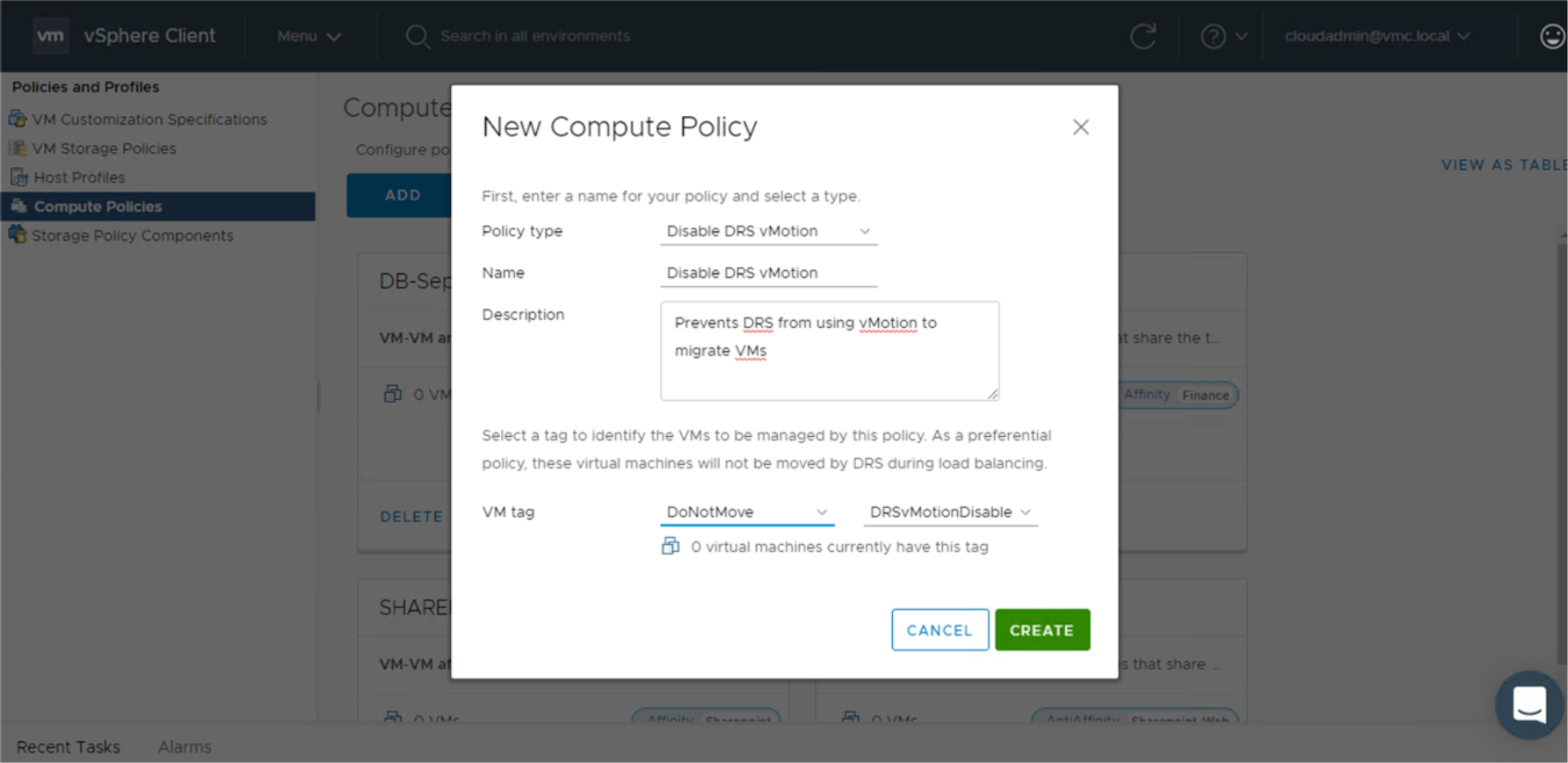
To apply the compute policy to a VM, browse to the VM in the vSphere Client inventory, right-click, and add the tag to the VM. The policy is applied to the VM during the next scheduled remediation.
You can create or delete, but not modify, a compute policy. If you delete a category tag used in the definition of the policy, the policy is also deleted.
